Ethics of Police Conduct
(Relevant for Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude)
(Reference: Static)
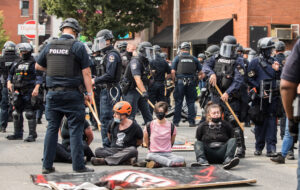
Police Misconduct and Brutality
Police misconduct and brutality represent significant ethical concerns that erode public trust and confidence in law enforcement organizations. Police misconduct encompasses unlawful or unethical actions by police officers, including corruption, abuse of authority, and evidence tampering, among others. Meanwhile, police brutality involves the excessive or unwarranted use of force by police officers, such as torture, deaths in custody, and lethal encounters.
The ethical dimensions of police misconduct and brutality can be accessed from various angles, including:
- Human Rights: Police misconduct and brutality infringe upon the basic rights of citizens, such as the right to life, liberty, dignity, equality, and justice. Furthermore, they violate international human rights standards, such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), and the Convention against Torture, among others.
- Rule of Law: These actions undermine the very foundation of a democratic society, which is the rule of law. They diminish the legitimacy and credibility of law enforcement agencies and foster a culture of impunity and lawlessness, wherein the police assume the roles of judge, jury, and executioner.
- Professionalism: Police misconduct and brutality corrode the professionalism, integrity, and morale of the police force. They reflect negatively on training, discipline, supervision, and leadership, putting pressure on honest officers to conform to unethical practices.
- Social Harmony: Police misconduct and brutality disrupt social harmony and cohesion by breeding feelings of resentment, fear, anger, and distrust among people, especially among marginalized and vulnerable populations. Moreover, they contribute to social conflicts, violence, and extremism, posing a threat to national peace and stability.
What do you mean by police reforms means?
- Police reforms aim to transform the values, culture, policies and practices of police organizations.
- It envisages police to perform their duties with respect for democratic values, human rights and the rule of law.
- It also aims to improve how the police interact with other parts of the security sector, such as the courts and departments of corrections, or executive, parliamentary or independent authorities with management or oversight responsibilities.
- Police come under the state list of schedule 7 of the Indian constitution.
Legal Reforms:
- The current legislation governing the police force requires revision and modernization. The Police Act of 1861, a relic from colonial rule, should be replaced with a new law that aligns with constitutional values and principles.
- Recommendations from various commissions and committees, including the National Police Commission, the Ribeiro Committee, the Padmanabhaiah Committee, the Malimath Committee, and the Prakash Singh case, among others, must be put into action.
Institutional Reforms:
- Mechanisms and processes ensuring accountability and oversight within the police force should be bolstered and streamlined.
- Political interference and influence on police operations should be minimized through measures that guarantee operational autonomy and secure tenure for police officers.
- Internal accountability tools, such as complaints authorities, vigilance departments, and disciplinary procedures, should be enhanced for greater effectiveness and transparency.
- External accountability mechanisms, such as the judiciary, legislature, human rights commissions, civil society, and media, should be made more accessible and responsive.
Capacity Building Reforms:
- Police personnel should receive training to equip them with the necessary skills, knowledge, and attitudes to perform their duties professionally, with integrity, and while respecting human rights.
- Upgrading and modernizing police infrastructure and equipment is essential to enable them to address emerging challenges and threats.
- Police welfare and well-being should be prioritized through adequate remuneration, incentives, facilities, and support.
Community Policing Reforms:
- Enhancing the relationship and interaction between the police and the community is crucial through community policing initiatives.
- Police should adopt a more participatory, collaborative, and service-oriented approach toward the public, rather than a coercive, confrontational, and authoritarian one.
- Involving the community in crime prevention, detection, resolution, and the maintenance of law and order is essential.
- Police should respect the diversity, dignity, and rights of the people while addressing their grievances and concerns.
Police misconduct and brutality are grave ethical issues that pose a serious threat to the democratic fabric and social harmony of the nation. They need to be addressed with utmost urgency and sincerity by implementing comprehensive and holistic reforms in the legal, institutional, capacity building and community policing aspects of the law enforcement agencies. Only then can the police force regain the trust and confidence of the people and fulfill its role as the protector and defender of the rights and liberties of the citizens.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What are the ethical implications of police misconduct and brutality?
Answer: The ethical implications are severe, including violations of human rights, undermining the rule of law, corroding professionalism within the police force, and disrupting social harmony.
Q2: How do police misconduct and brutality affect marginalized and vulnerable populations?
Answer: These unethical practices foster fear, distrust, and resentment among marginalized communities, contributing to social conflicts and affecting national peace and stability.
Q3: What is the significance of the Police Act of 1861 in modern law enforcement?
Answer: The Police Act of 1861 is outdated and colonial in nature; it does not align with modern democratic values, human rights, or the rule of law, necessitating comprehensive legal reforms.
Q4: How can community policing improve the relationship between law enforcement and the public?
Answer: Community policing fosters a collaborative and participatory relationship between police and the community, focusing on service over coercion and involving citizens in maintaining law and order.
Q5: What role do external accountability mechanisms, like human rights commissions and media, play in police oversight?
Answer: External accountability mechanisms serve as checks on police actions, ensuring transparency, investigating misconduct, and encouraging adherence to legal and ethical standards.
Related Blogs …
 |
 |
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques.
Police misconduct, police brutality, ethics, human rights, rule of law, police reforms, accountability, community policing, legal reforms, Police Act of 1861, National Police Commission, Indian Constitution, social harmony

Choose The Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “which optional subject is the best?” and “which optional subject is the most scoring?” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher, is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains, which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular
Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers.”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional, you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey, potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher. Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques. Sociology, Social theory, Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Sociology Optional Syllabus.
Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Sociology Syllabus, Sociology Optional, Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Course, Sociology Teacher, Sociology Foundation, Sociology Foundation Course, Sociology Optional UPSC, Sociology for IAS,
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology
Find More Blogs
|
Scope of the subject and comparison with other social sciences |
|||
|
|
|
|
Modernity and social changes in Europe |


