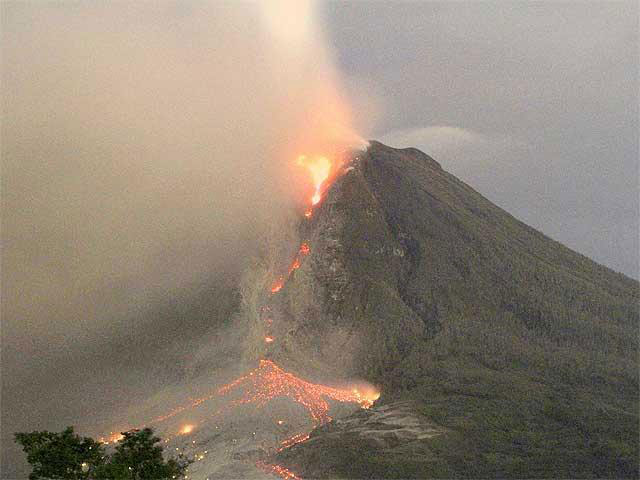
Mount Sinabung: Volcanic eruption in Indonesia’s
Why In News?
Recently, Mt. Sinabung, which is an active volcano on Indonesia’s Sumatra island has erupted.

Background:
- The volcano became active in 2010, erupting after nearly 400 years of inactivity.
- According to the information maintained by the National Museum of Natural History’s Global Volcanism Program another eruptive phase for the volcano began in September 2013, which continued uninterrupted until June 2018.
- Mount Sinabung, which is 2,460 m high, is among Indonesia’s most active volcanoes but had been inactive for four centuries before its 2010 eruption.
- Indonesia is home to nearly 130 active volcanoes, due to its position on the “Ring of Fire”, or the Circum-Pacific Belt.
What is Ring of Fire?
- It is also called as the Circum-Pacific Belt, is a path along the Pacific Ocean characterized by active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes.
- It traces boundaries between several tectonic plates—including the Pacific, Cocos, Indian-Australian, Nazca, North American, and Philippine Plates.
- It is home to about 75 per cent of the world’s volcanoes and about 90 per cent of its earthquakes.
- In the realm of Ring of Fire, the tectonic plates overlap at convergent boundaries which results in subduction zones. Here, the plate which is below at the convergent boundary is pushed down, or subducted, by the plate above. As the rock is subducted, it melts and becomes magma. The abundance of magma so near to Earth’s surface gives rise to conditions ripe for volcanic activity.
About volcanic eruptions:
- A volcano is a vent or fissure in Earth’s crust through which lava, ash, rocks, and gases erupt.
- A volcano can be active, dormant or extinct. An eruption takes place when magma (a thick flowing substance), formed when the earth’s mantle melts, rises to the surface.
- The magma is lighter than solid rock, it is able to rise through vents and fissures on the surface of the earth. After it has erupted, it is called lava.
- Not all volcanic eruptions are explosive since explosivity depends on the composition of the magma.
- When the magma is runny and thin, gases can easily escape it, in which case, the magma will flow out towards the surface and if the magma is thick and dense, gases cannot escape it, which builds up pressure inside until the gases escape in a violent explosion.
Consequences of Volcanic Eruption:
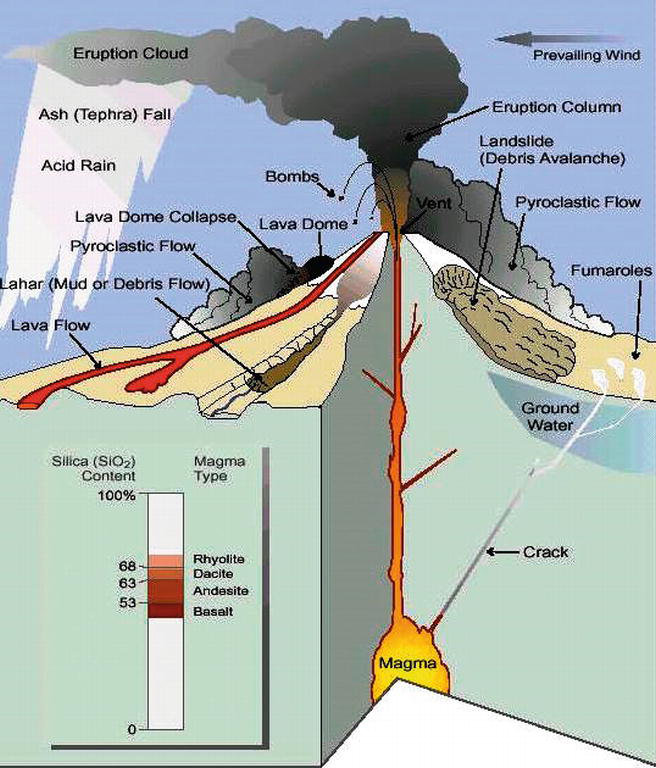
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the most common cause of death from a volcano is suffocation, making people with respiratory conditions such as asthma and other chronic lung diseases especially susceptible.
- Population living in close vicinity to the volcano, or in low-lying areas downwind, are also at higher risk in case of an explosion since the ash may be gritty and abrasive and small ash particles can scratch the surface of the eyes.
- The volcanic eruptions can result in additional threats to health such as floods, mudslides, power outages, drinking water contamination and wildfires.
For more such notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel.
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC –Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php



