Exploring the Depths and Implications of Internet Shutdown in India: A Comprehensive Overview.
Relevant for General Studies Paper | Polity | Prelims/Mains.

Internet Shutdown: is it derogatory to fundamental rights?
Internet shutdown involve the intentional disruption of internet or electronic communications, rendering them inaccessible or effectively unusable for a specific population or within a particular location. This is often done to exert control over the flow of information and can impact mobile internet, broadband internet, or both.
On September 23, 2023, the Manipur government declared the restoration of full internet access, attributing it to an “improved” law and order situation. This marked the end of India’s second-longest internet blackout, lasting over 143 days since May 3. The announcement was met with relief by citizens, ranging from students planning their return to Manipur to aid workers in urgent need of essential supplies.
Provisions related to internet shut downs.Section 5(2) of the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, in conjunction with the Temporary Suspension of Telecom Services (Public Emergency and Public Safety) Rules, 2017:
Section 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure:This section grants authority to a district magistrate, sub-divisional magistrate, or any other executive magistrate specially delegated by the state government to issue orders preventing or halting any nuisance or disturbance of public tranquility. Such orders may encompass the suspension of internet services in a specific area for a specified period. |
Impacts of Internet Shutdown.
Violation of Fundamental Rights: Internet shutdowns infringe upon Fundamental Rights as outlined in Article 19(1)(a) and Article 19(1)(g). Constitutional protection under Article 19(1)(a) and Article 19(1)(g) safeguards the freedom of speech and expression and the freedom to practice any profession over the medium of the internet, as affirmed by the Supreme Court in the Anuradha Bhasin vs Union of India case (2020).
Internet shutdown also contravene the Right to Information, recognized as a Fundamental Right under Article 19 by the Supreme Court in the Raj Narain vs State of UP (1975) case. Furthermore, the Right to Internet, declared a Fundamental Right under Article 21 by the Kerala High Court in the Faheema Shirin v. State of Kerala case, is violated by internet shutdowns.
Economic Consequences: Internet shutdown can result in significant economic repercussions. Businesses relying on the internet for operations, sales, and communication may experience financial losses, with startups and small businesses being particularly susceptible. According to Top10VPN, India incurred a loss of Rs 2,091 crore ($255.2 million) in the first half of 2023 due to internet shutdowns.
Disruption of Education: Numerous educational institutions utilize online platforms for teaching and learning. Internet shutdown disrupt access to educational resources, posing challenges for students to continue their studies.
Trust and Censorship Concerns: Internet shutdown can diminish trust in government and authorities, raising concerns about censorship and a lack of transparency.
Impediment to Disaster Response: Internet shutdown hinder communication and coordination, especially during emergencies and crises. A UN-backed report has emphasized that shutting down the internet affects people’s safety and well-being by impeding information flow and humanitarian assistance.
Disruption in Health Care: Studies reveal significant impacts of internet shutdowns on health systems, including hindrances to urgent medical care, disruption of essential medicine delivery, and maintenance of equipment, as well as limitations on the exchange of health information among medical personnel and disruptions in essential mental health assistance.
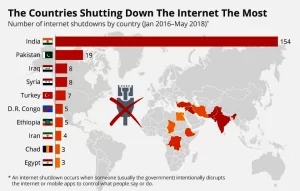
International Repercussions: Internet shutdown can draw international attention and condemnation, potentially harming a country’s reputation and relationships with other nations. India holds the record for the most internet shutdowns globally. In the first half of 2023, India ranked second globally for internet shutdowns. According to a report by the US digital rights advocacy group Access Now, India accounted for 58% of all documented shutdowns globally.
Impact on Journalism and Reporting: Journalists rely on the internet to report on events and share news with the public. Internet shutdowns can impede their ability to gather and disseminate information, compromising the public’s right to know. The Right to Freedom of the Press is a Fundamental Right declared by the Supreme Court in the Indian Express vs Union of India (1986) and Bennett Coleman vs Union of India (1972) cases.
Arguments Regarding Internet Shutdown.
Arguments in Favor:
- Internet shutdown are often implemented to prevent the dissemination of hate speech and false information that might incite violence and riots. As an illustration, the government declared an internet shutdown in Delhi NCR following the farmers’ protest on Republic Day to counter misinformation and maintain law and order.
- Another purpose of internet shutdowns is to restrain the organization and mobilization of protests that could disrupt public order and security. For instance, the government enforced internet shutdown in Kashmir and other parts of the country after the abrogation of Article 370 to prevent any anti-national activities and separatist movements.
- The safeguarding of national security and sovereignty from external threats and cyber attacks is cited as a rationale for internet shutdowns. During the standoff with China, the government suspended internet services in some border areas to prevent espionage or sabotage.
- Furthermore, internet shutdowns are considered a means to regulate the distribution and consumption of content that might be harmful or offensive to certain groups or individuals. An instance of this is when the government blocked internet access in specific regions to prevent the circulation of objectionable images or videos.
Arguments against:
- Internet shutdown erode democratic principles and accountability by hindering citizens’ access to information, expression of opinions, engagement in public debates, and holding authorities accountable for their actions.
- They also empower authoritarian governments to silence dissenting voices and cultivate distorted information echo chambers. Critics contend that internet shutdowns are ineffective and counterproductive, failing to address the root causes of the issues they aim to resolve.
For instance, rather than halting violence or terrorism, internet shutdowns tend to intensify anger and resentment among affected populations. Additionally, they do not deter misinformation or hate speech; instead, they create information vacuums that can be exploited by malicious actors.
- Internet shutdowns are arbitrary and prone to abuse, often imposed without due process, transparency, or judicial oversight. Frequently, these shutdowns are ordered by local authorities lacking the legal authority to do so.
- Moreover, internet shutdowns lack clear and objective criteria, duration, and scope, leaving them susceptible to political interference and violations of human rights.
What could be done?
- Enhancing the Existing Framework: Strengthening the legal and regulatory framework overseeing internet shutdowns, ensuring they are employed as a last resort in line with international human rights standards. The government ought to revise the outdated and vague Telegraph Act and its rules to align with constitutional and human rights standards.
- Ensuring Authority Accountability: Enhancing transparency and accountability of authorities responsible for ordering and implementing internet shutdowns, while establishing effective remedies for those adversely affected by such actions.
- Exploring Alternative Measures: The government should explore less intrusive measures to address law-and-order disruptions, communal violence, terrorist threats, examinations, and political instability. Options include selectively blocking websites or content, issuing warnings or advisories, engaging with civil society and media, or deploying additional security forces.
- Compliance with Supreme Court Guidelines: Authorities should adhere to the directives of the Supreme Court, as outlined in the Anuradha Bhasin case (2020). The Supreme Court’s guidelines emphasize that internet suspension should be temporary, proportionate, and subject to judicial review under the Suspension Rules.
Reference: Indian Express
Related Blogs…
 |
 |
Frequently Asked Questions:
Question 1: Define Internet Shutdown and its common purpose.
Answer: An internet shutdown involves the intentional disruption of internet or electronic communications, often executed to control information flow and maintain law and order during perceived crises.
Question 2: Which act and section empower the Indian government to authorize the suspension of internet services?
Answer: The Indian government is empowered to authorize the suspension of internet services under Section 5(2) of the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, and the Temporary Suspension of Telecom Services (Public Emergency and Public Safety) Rules, 2017.
Question 3: What fundamental rights are often infringed upon during an internet shutdown as per the Indian Constitution?
Answer: Internet shutdown infringe upon Fundamental Rights such as the freedom of speech and expression and the freedom to practice any profession over the internet medium, safeguarded by Article 19(1)(a) and Article 19(1)(g) of the Indian Constitution, respectively.
Question 4: How do internet shutdown impact the economy, providing a recent statistical insight?
Answer: Internet shutdown can have substantial economic impacts, hindering businesses and communications; for instance, India incurred a loss of Rs 2,091 crore ($255.2 million) due to internet shutdowns in the first half of 2023.
Question 5: Enumerate some of the arguments in favor and against internet shutdown.
Answer: In favor, arguments often cite the prevention of misinformation spread, maintenance of law and order, and national security. Contrarily, arguments against point towards erosion of democratic principles, empowerment of authoritarian tendencies, and abuse due to lack of clear criteria and oversight.
Question 6: Name a case where the Supreme Court affirmed the importance of internet freedom relating to the fundamental right of speech and expression.
Answer: The Supreme Court affirmed the importance of internet freedom in the Anuradha Bhasin vs Union of India case in 2020.
Question 7: What are some alternatives that can be explored instead of imposing complete internet shutdowns, as suggested?
Answer: Alternative measures include selectively blocking harmful content, issuing public warnings or advisories, engaging with civil society, deploying additional security forces, and ensuring that shutdowns, if implemented, are temporary, proportionate, and subject to judicial review.
Question 8: Which global position did India hold regarding internet shutdowns in the first half of 2023, and cite a related statistic.
Answer: India ranked second globally for internet shutdown in the first half of 2023, accounting for 58% of all documented shutdowns worldwide according to a report by Access Now.
GS Related Practices Questions…
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques.
META TAGS:
Internet Shutdown, Internet Shutdown upsc, Internet Shutdown in India, Internet Shutdown in Manipur, Fundamental Rights, India, Economic Impact, Education, Health Care, National Security, Law and Order, UPSC, Civil Services, Anuradha Bhasin Case, Telegraph Act, Temporary Suspension, Legal Framework, Freedom of Speech, Access to Information, Digital India, Online Censorship, Governance, Transparency, Accountability, Democracy

Why Vikash Ranjan’s Classes for Sociology?
Proper guidance and assistance are required to learn the skill of interlinking current happenings with the conventional topics. VIKASH RANJAN SIR at TRIUMPH IAS guides students according to the Recent Trends of UPSC, making him the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology Optional UPSC.
At Triumph IAS, the Best Sociology Optional Coaching platform, we not only provide the best study material and applied classes for Sociology for IAS but also conduct regular assignments and class tests to assess candidates’ writing skills and understanding of the subject.
Choose The Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “which optional subject is the best?” and “which optional subject is the most scoring?” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher, is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains, which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular
Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers.”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional, you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey, potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher. Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques. Sociology, Social theory, Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Sociology Optional Syllabus.
Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Sociology Syllabus, Sociology Optional, Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Course, Sociology Teacher, Sociology Foundation, Sociology Foundation Course, Sociology Optional UPSC, Sociology for IAS,
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
🔎https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology
Find More Blogs…
| Compare and contrast Karl Marx’s and Max weber’s | Karl Marx- Historical Materialism |
| Talcott Parsons : Social system | Scope of the subject and comparison with other social sciences |