Relevance: Mains: G.S paper III: Economy
Introduction:
• This transition is so compelling that it is being called Industry 4.0 to represent the fourth revolution that has occurred in manufacturing. Industry 4.0 is signalling a change in the traditional manufacturing landscape. Industry 4.0 encompasses three technological trends driving this transformation: connectivity, intelligence and flexible automation.

Evolution process of industrial revolution:
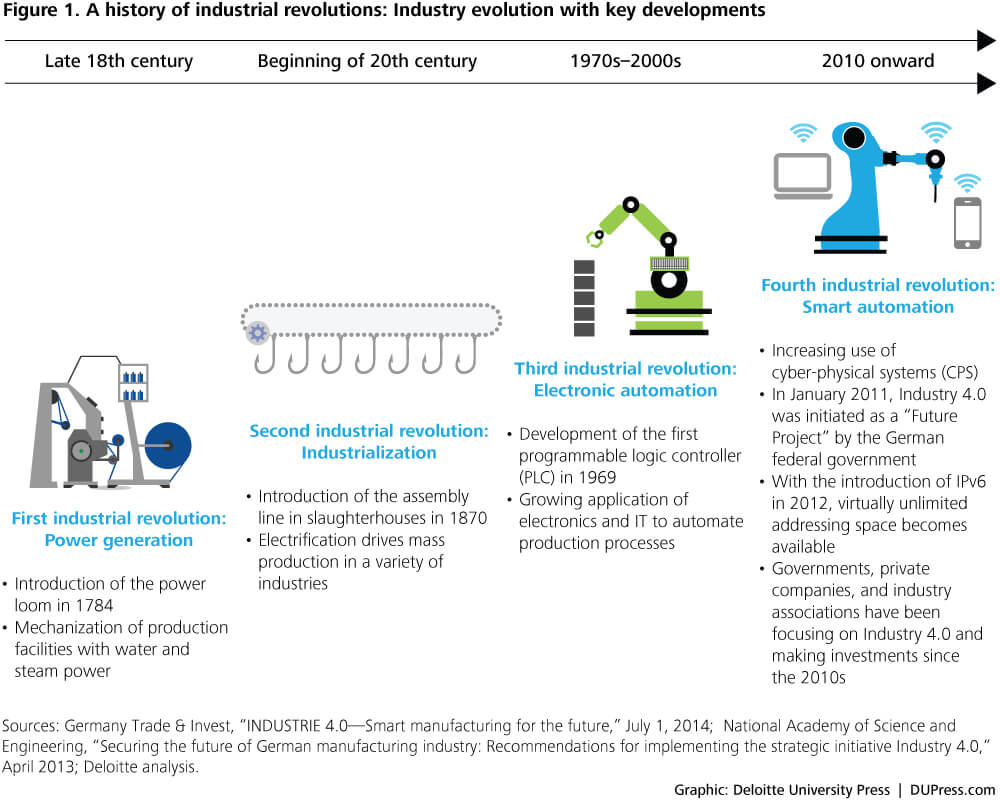
• The first industrial revolution came with the advent of mechanisation, steam power and water power.
• The second industrial revolution revolved around mass production and assembly lines using electricity.
• The third industrial revolution came with electronic and IT systems and automation.
• The fourth industrial revolution is associated with cyber-physical systems.

What about the Industry 4.0?
• Industry 4.0 describes the growing trend towards automation and data exchange in technology and processes within the manufacturing industry, including:
- The Internet of Things (IoT),
- The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT),
- Cyber-physical Systems (CPS),
- Smart Manufacturing,
- Smart Factories, Cloud Computing,
- Additive Manufacturing, Big Data, Robotics,
- Cognitive Computing,
- Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain etc.
• This automation creates a manufacturing system whereby the machines in factories are augmented with wireless connectivity and sensors to monitor and visualise an entire production process and make autonomous decisions.
• It is further estimated that wireless connectivity and the augmentation of machines will be greatly advanced with the full rollout of 5G. This will provide faster response times, allowing for near real-time communication between systems.

Digital twin technologies:
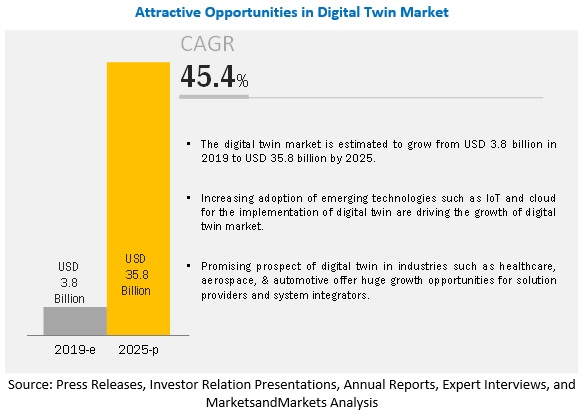
• The fourth industrial revolution also relates to digital twin technologies. These digital
technologies can create virtual versions of real-world installations, processes and applications. This can then be robustly tested to make cost-effective decentralised decisions.
• These virtual copies can then be created in the real world and linked, via the Internet of Things allowing for cyber-physical systems to communicate and cooperate with each other and human staff to create a joined up real-time data exchange and automation process for Industry 4.0 manufacturing.
• As Industry 4.0 unfolds, computers are connected and communicate with one another to ultimately make decisions without human involvement. A combination of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things and the Internet of Systems make Industry 4.0 possible and the smart factory a reality.
• As a result of the support of smart machines that keep getting smarter as they get access to more data, our factories will become more efficient and productive and less wasteful.
• Ultimately, it is the network of these machines that are digitally connected with one another which create and share information that results in the true power of Industry 4.0.
Radical Pace of Innovation:
• Innovation is fundamentally undergoing a radical change. Wherever we turn in the manufacturing world, the technological revolution immerses us.
• The scale, scope, and complexity are things we have certainly never experienced. It is exposing us to exponential technologies.
• We seem to have caught up in such levels of velocity, scope, and systems impact –it is seemingly exponential, occurring at faster rates of change. Companies are radically overhauling entire systems of production, management, and governance on a constant basis of change.
• We have unprecedented processing power, storage capacity, and access to various avenues of knowledge. These are being combined with emerging technology in fields such as artificial intelligence, robotics, 3D printing, nanotechnology, biotechnology, material science, and quantum computing. It is creating fresh challenges and opportunities within innovation.
• The world is facing greater disruption and an increasing innovation pace and actually caught up in a very revolutionary period.
• The days of simple product innovation are dwindling. Currently, the technology, talent, and new innovation ecosystems are emerging; building greater complexities into our final innovation offerings.
• Intelligent automation and technology are fueling this new industrial revolution. And this unprecedented, exponential pace of change is increasingly reliant on collaborative platforms to realise the result which is more radical innovations.
Emerging Digital Business Models:
• We need to appreciate new digital business models and their impact. We are increasingly reliant on digital engineering and science.
• There is scope to have radically different product development and processes to manage.
• These are multiplying by this rate of industrial change. The traditional supply chain has a very different potential when factories and operations become highly connected and start operating as Industry 4.0 entities.
• The new business models will emerge from the way they can be operated, be responsive in the supply networks. All this requires digital management. As we connect more, the customer experiences can hugely benefit. We can target, sell, and market on greater connecting knowledge platforms. We can understand channel choice and provide more tailored presales and post-sales support to manage the entire lifecycle as we continue to build the connected industry 4.0 ecosystems.
• Further, Blockchain technology is not only disrupting banking and finance, but it also has the potential to impact many industries and community as a whole.
• For instance, this technology can enable a car to respond as per the need by installing a digital wallet based on Blockchain technology. This wallet works by logging all transactions made involving the vehicle, including maintenance, modifications, charging or filling up gas.
• It makes it possible to predetermine the total cost of ownership and calculate return on investment for the car on a very detailed level.
Industry 4.0 Post COVID-19:
• Industry 4.0 is not only as relevant as it was before the global COVID-19 emergency; it is actually far more relevant moving forward. The world is gripped by the pandemic. The global supply chain is experiencing a level of disruption that has never been seen before.
• Some manufacturers have ceased production completely, some have seen greatly reduced demand and others have seen a huge increase in demand. Every manufacturer is impacted by this crisis in some way and for many this poses an existential threat.
• We have noticed during COVID-19 pandemic that how exhibitions are getting ready on virtual spaces.
How physical conferences are converting into digital webinars?
• Prior to the crisis, Industry 4.0 was an area of great interest to many manufacturers. At this point, it probably seems insensitive and inappropriate to discuss Industry 4.0 in the way it was discussed pre-crisis. The business drivers of Industry 4.0 pre-crisis were focused on competitive advantage, cost reduction, productivity, sustainability and innovation.
• The goal was to make smooth businesses to run better. The focus for many manufacturers now is survival first and foremost and beyond that, damage limitation. The immediate financial impact on manufacturers is already resulting in a huge reduction in non-essential spending and investments. Many Industry 4.0 solutions currently being considered or being deployed fall into the category of non-essential business activities.
• Now, the bigger question is-Is Industry 4.0 relevant anymore? If it is relevant, why and what role does it have to play moving forward? We believe Industry 4.0 is not only as applicable as it was before but it is actually far more relevant moving forward.
• The priorities for most manufacturers today fall into three distinct Stages:
o Stage 1 – Survival;
o Stage 2 – Recovery;
o Stage 3 – Business as usual in the new postcrisis paradigm.
• The goal for all manufacturers will be to get to Stage 3 as soon as possible at the lowest cost. In defining the operating model for Stage 3 they will factor-in lessons learnt from the crisis and try to build a more resilient and agile business.
• As we believe one of the major weaknesses is a lack of real-time visibility across the business. Visibility that is essential to support critical business decisions.
• Another key learning from the crisis will be driven by manufacturers’ reliance on human capital and the impacts of social distancing. If we go one level deeper than the supply chain view, then manufacturing in particular will be highlighted as a big area for improvement.
• During the crisis, production plans would have been changing on a much higher frequency as a result of changing demands and availability of raw materials, key staff and assets. Manufacturing has a much higher volume and frequency of transaction than the supply chain.
COVID-19 Leading to Digital Transformation:
• The integration of digital infrastructure to streamline public health to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic is very crucial in the context of epidemic forecasting and decision-making, one such example in India is the Aarogya Setu app by Government of India.
• This application is official COVID-19 tracker. This explains that digital contact tracing is conferring a new form of immunity–digital immunity.
• The fastest scalable solution to India’s COVID-19 challenge was to employ digital technology for diagnosis and for contact tracing. Aarogya Setu app can also be tapped for providing telemedicine, especially in remote parts, during this moment of crisis.
• This digital infrastructure implementation increasingly fuels the digital transformation initiatives within an organisation as well. But due to the pandemic, the transition will see significant changes in industries especially in technology, food delivery services, customer service, and virtual events. In the present situation, we are seeing major occurrences worldwide, including soaring adoption of online services, an enormous requirement for internet services, and enhanced connectivity among industries, regardless of their sizes.
• The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated the value of IT and digital transformation across industries and businesses and they must utilise this time to speed up the transition.
• It has been demonstrated in the enhanced corporate ability of long-distance collaborative work, wide recognition of the value of digital transformation and information technology among all employees, and the ability to market online and business development.
• In the time of Coronavirus crisis, Digital Industry 4.0 plays a vital role in envisioning and modeling outbreaks. As the pandemic continues to spread around the world, it will become imperative for organisations to look for new solutions or ways to stay ahead of the competition. Because most enterprises will fail to spot their financial targets due to supply-chain disruptions and lowered customer demand.
COVID-19 effect to the manufacturing sector:
• The COVID-19 pandemic hit manufacturers in an unexpected and unprecedented way. For the first time in modern manufacturing history, demand, supply and workforce availability are affected globally at the same time.
• Social distancing and employee safety measures put an additional level of pressure on manufacturers, as 40-50% of their workforce will be unavailable to perform their functions on-site. While office employees and knowledge workers are able to shift to remote work as the default operating mode, most factories are simply not designed to be managed remotely and lack the digital tools and infrastructure needed to support such activities.
Way ahead:
• However, this situation must be viewed as an opportunity and companies must focus on digital infrastructure. Organisations that adapt their technological capacity and investments on digital platforms can alleviate the impact of the COVID-19 and keep their businesses running in the long term.
• Many organisations may adopt remote working agreements as strategies to reduce costs, improve productivity, and increase worker satisfaction.
• Many manufacturers are increasing efforts to equip their human workers with digital connected-worker tools that incorporate safety checks into workflows, ensure collaboration with colleagues when physical contact is off the cards, and other such processes that ultimately balance business continuity and employee health.
Conclusion:
• This is also the dawn of a new era where ‘frontline’ workers and desk workers are harmonised with tools that can support the flow of collaboration and data, where something that happens on the factory floor initiates a communication or workflow in the back office.
• Although, the concept of using connected-worker technology to empower workers around safety, quality and productivity may be heightened right now, it will still be just as critical to build business resiliency after this pandemic is over.
• What most of us consider normal has already fundamentally shifted. Manufacturers who understand and act on this new normal will have ample opportunities for growth in this era of Industry 4.0.
For more such notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel.
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC –Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php



