Unlocking Inclusive Growth in India through Microfinance: Opportunities and Challenges.
Relevant for General Studies Paper | Economics | Prelims/Mains.

Microfinance: an opportunity to inclusive growth.
A quatrain from the 13th century Telugu literature underscores the significance of having a lender, doctor, flowing river, and righteous people in a village. In the contemporary context, microfinance has evolved into a critical means to fulfill these essential requirements.
Microfinance has emerged as a pivotal tool for fostering inclusive and sustainable growth in India. The extensive rural expanse of India necessitates a financial ecosystem that is attuned to the needs of communities residing in remote areas.
The inception of the microfinance concept traces back to the Self Help Group Bank Linkage Programme (SHG-BLP), which originated as a result of an action research project conducted by MYRADA in 1989, commissioned by Nabard. The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) initiative to connect informal groups with banks for facilitating micro deposits and loans brought the SHG-BLP into fruition.
The essence of India resides in its rural hinterlands, which also serve as the economic powerhouse of the country. Through fostering financial inclusion, empowering women, and ensuring digital participation, microfinance is poised to play a substantial role in India’s journey towards becoming a global powerhouse.
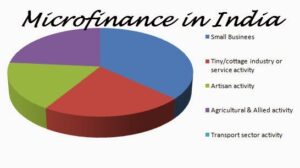
State of Microfinance in India.
- Microfinance, as per a study by the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER), contributes to approximately 130 lakh jobs and constitutes 2% of our Gross Value Added (GVA).
- This approach has the capability to extend its reach to all 6.3 crore unincorporated and non-agricultural enterprises. Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has defined microfinance as collateral-free loans provided to households with an annual income of up to Rs. 3 lakh.
- Securing the future of microfinance can be achieved by transitioning all microloans to the formal sector, facilitated through channels like banks or microfinance institutions.
Contribution of micro finance to India.
- Boosting Entrepreneurship: Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) extend small loans to individuals without access to conventional banking services. This support is vital for fostering entrepreneurship and nurturing the development of small businesses in India, contributing significantly to economic growth and job creation.
- Financial Inclusion: The role of MFIs in enhancing financial inclusion is noteworthy, offering access to credit and various financial services to individuals excluded from the conventional banking system. This, in turn, facilitates savings, investments in education and healthcare, and the initiation of independent business ventures.
- Poverty Reduction: Microfinance emerges as a potent tool for poverty reduction in India by providing small loans to impoverished individuals lacking access to formal banking channels. These loans enable them to initiate income-generating activities, thereby elevating their standard of living.
- Empowering Women: A pivotal aspect of microfinance is its contribution to empowering women in India, a demographic often constrained in financial access and disproportionately affected by poverty. Through granting access to credit and financial services, microfinance facilitates women’s economic independence and enhances their societal standing.
- Supporting Rural Development: Microfinance plays a crucial role in supporting rural development in India by extending small loans to farmers and other rural entrepreneurs. This financial support contributes to improved agricultural productivity, job creation, and overall economic development in rural regions.
Challenges with Microfinance in India.
- Over-Indebtedness: A significant hurdle facing microfinance in India is the issue of over-indebtedness, wherein borrowers struggle to repay multiple loans obtained from various microfinance institutions. This predicament can result in defaults, adversely affecting the borrower’s creditworthiness, and, in severe cases, leading to tragic outcomes such as suicide.
- High-Interest Rates: Microfinance institutions impose high-interest rates, driven by the substantial cost associated with servicing small loans. This practice can ensnare borrowers in a debt trap, making it challenging for them to fulfill their repayment obligations.
- Lack of Financial Literacy: The majority of microfinance borrowers in India hail from rural areas, often characterized by low literacy rates and limited financial literacy. This lack of understanding can pose difficulties in comprehending the loan terms and conditions, fostering misunderstandings and disputes.
- Infrastructure Challenges: Microfinance institutions operate in remote and rural regions where infrastructure deficiencies are prevalent. This can result in communication hurdles, transportation challenges, and difficulties in accessing financial services.
- Political Interference: Interference by political entities in the operations of microfinance institutions can compromise their effectiveness and create an unfavorable operating environment.
- External Shocks: Microfinance borrowers are susceptible to external shocks such as natural disasters, economic downturns, and pandemics. These unforeseen events can disrupt their ability to repay loans, leading to defaults and financial strain.
- Lack of Regulation: While microfinance institutions fall under the regulatory purview of the Reserve Bank of India, the absence of comprehensive state-level regulation introduces inconsistencies in their operations across different states in India.
What could be done to leverage microfinance for inclusive growth?
- Strengthening the Regulatory Framework: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) must continue its vigilant oversight and regulation of the microfinance sector to ensure its fair and transparent operation. Additionally, the RBI should explore the implementation of regulations specifically targeting the high-interest rates levied by Microfinance Institutions (MFIs).
- Promoting Financial Literacy: Enhancing financial literacy among microfinance borrowers is imperative to empower them in making well-informed decisions regarding borrowing and repayment. Regular financial literacy programs conducted by MFIs can play a pivotal role in educating clients about aspects such as savings, credit, insurance, and investment.
- Encouraging Innovation: Fostering innovation in product development, delivery mechanisms, and technology adoption is crucial for the microfinance sector in India. The adoption of technologies like mobile banking and digital lending platforms can significantly broaden the accessibility of financial services while reducing delivery costs.
- Promoting Partnerships: Collaboration between the government, MFIs, and other stakeholders is essential to address sector challenges effectively. Strategic partnerships, particularly between MFIs and banks, can enhance the provision of financial services to microfinance clients.
- Addressing the Issue of Over-Indebtedness: Mitigating over-indebtedness, a prominent concern in the microfinance sector, necessitates the establishment of a credit information system. This system would track the borrowing history of microfinance clients, preventing them from taking loans beyond their capacity to repay.
- Ensuring Social Impact: Microfinance should be viewed as a tool for poverty reduction and social empowerment. The sector should prioritize delivering positive social impact by extending financial services to the poorest and most vulnerable segments of the population.
Reference: The Hindu
Related Blogs…
 |
 |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Question: What is the primary objective of microfinance in the context of rural India?
Answer: To foster inclusive and sustainable growth by facilitating financial inclusion and empowering women.
2. Question: When and as a result of whose research project did the Self Help Group Bank Linkage Programme (SHG-BLP) originate?
Answer: Originated in 1989 as a result of an action research project conducted by MYRADA, commissioned by Nabard.
3. Question: What is the recent definition of microfinance according to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)?
Answer: Microfinance refers to collateral-free loans provided to households with an annual income of up to Rs. 3 lakh.
4. Question: What percentage of Gross Value Added (GVA) does microfinance contribute to, according to the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER)?
Answer: Microfinance contributes to approximately 2% of India’s GVA.
5. Question: How does microfinance contribute to poverty reduction in India?
Answer: By providing small loans to impoverished individuals, enabling them to initiate income-generating activities and improve their living standards.
6. Question: What significant role does microfinance play in empowering women in India?
Answer: It provides access to credit and financial services, facilitating women’s economic independence and enhancing their societal standing.
7. Question: Identify one major challenge associated with high-interest rates in microfinance.
Answer: High-interest rates can lead borrowers into a debt trap, making it difficult to fulfill their repayment obligations.
8. Question: What role can promoting financial literacy play in leveraging microfinance?
Answer: It can empower borrowers to make informed decisions regarding borrowing and repayment, enhancing the effectiveness and impact of microfinance.
9. Question: How can over-indebtedness in the microfinance sector be addressed effectively?
Answer: By establishing a credit information system to track microfinance clients’ borrowing history and prevent over-borrowing.
10. Question: What strategy could be adopted to expand the accessibility of financial services in microfinance?
Answer: Adopting technologies like mobile banking and digital lending platforms to enhance accessibility and reduce delivery costs.
GS Related Practices Questions…
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques.
META TAGS:
Microfinance, Inclusive Growth, India, Financial Inclusion, Entrepreneurship, Women Empowerment, Rural Development, Over-Indebtedness, Regulatory Framework, Financial Literacy, Innovation, UPSC, Economy

Why Vikash Ranjan’s Classes for Sociology?
Proper guidance and assistance are required to learn the skill of interlinking current happenings with the conventional topics. VIKASH RANJAN SIR at TRIUMPH IAS guides students according to the Recent Trends of UPSC, making him the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology Optional UPSC.
At Triumph IAS, the Best Sociology Optional Coaching platform, we not only provide the best study material and applied classes for Sociology for IAS but also conduct regular assignments and class tests to assess candidates’ writing skills and understanding of the subject.
Choose The Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “which optional subject is the best?” and “which optional subject is the most scoring?” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher, is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains, which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular
Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers.”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional, you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey, potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher. Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques. Sociology, Social theory, Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Sociology Optional Syllabus.
Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Sociology Syllabus, Sociology Optional, Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Course, Sociology Teacher, Sociology Foundation, Sociology Foundation Course, Sociology Optional UPSC, Sociology for IAS,
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
🔎https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology
Find More Blogs…
| Compare and contrast Karl Marx’s and Max weber’s | Karl Marx- Historical Materialism |
| Talcott Parsons : Social system | Scope of the subject and comparison with other social sciences |