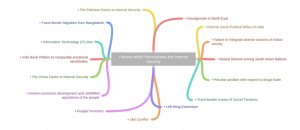
Factors which Necessitates the Internal Security:
India possesses Internal Security threats from various sources, and the reasons for it are very complex to comprehend. However, a lucid understanding of all the factors that create internal security compulsion for India is important. These factors are as follows:
- Mutual Distrust among South Asian Nations: The consolidation of South Asian nations into their new identities had resulted into mutual distrust in their relations. Tensions between pluralist democratic governments and unitary form of non-pluralist governments in the sub continent further add to the imbalances and tensions.
- Trans-border impact of Social Tensions: South Asia consists of numerous ethnic, religious and linguistic groups which often indulge in violent clashes among themselves. Such violence is transnational in nature and impacts the internal security situation across the border. Traditional linkages of friendship and inter- action amongst people have become competing arrangements for aiding and abetting subversion, terrorism and insurgencies.
- Peculiar position with respect to drugs trade: Two of the three major narcotic centres of the world, the Golden Crescent in the North West and the Golden Triangle in the East have made India vulnerable to drug trafficking.
- Diverse Socio-Political Milieu of India: The domestic dynamic of India’s Internal Security is reflected in its socio-political milieu consisting of variety of communities, castes, ethnicities, religion, languages, customs and traditions, all operating in a dynamic environment.
- Failure to integrate diverse sections of Indian society: Indian democratic state has had various failures in welding the various sections of society together. This has created conflict situation to the point of violence; and issues of ethno-nationalism and identity are an outcome of this failure only.
- Vote Bank Politics to manipulate emotional sensitivities: Various political parties have manipulated the emotional sensitivities of different communities in order to gain their vote bank. This has created communal tensions and led to radicalization of individuals.
- Uneven economic development and unfulfilled aspirations of the people: The unjust distribution of economic development and development benefits has driven affected groups to assert themselves and the main target is government, both local and central.
- Trans-Border Migration from Bangladesh: It is a major factor for the problems in Assam and other areas of the North East. Their transgression into land matters and provision of cheap labour by them is a cause of social and economic insecurity for local communities and a cause of tension and violence.
- Information Technology (IT) War: The modern day IT has revolutionized warfare and provided means to the underworld to expand their reach for criminal activities without direct physical involvement.
- The China Factor to Internal Security: The Chinese are believed to have resorted to giving financial aid, arms and sanctuaries to Naga, Mizo and Meitei extremists in the North Eastern states. China is also trying for a strategic containment of India by forming regional alliances and arming India’s neighbors Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan.
- The Pakistan Factor to Internal Security: Over the years, Pakistan has supported state sponsored terrorism to create unrest in India. Pakistan has established bases in Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and the Middle East- the plan aims at encirclement of India. This combined with the upsurge in Islamic Terrorism at the global level with its epicenter in Central Asian Republic, Afghanistan and Pakistan is likely to have persistent affect on India’s internal
- J&K Conflict: The conflict in J&K has provided ingression to foreign extremist in the country. The people in the state and the minority community at large have been alienated by the Indian State due to the violent and less developed situation in J&K.
- Insurgencies in North East: North-East is an extremely heterogeneous region with high level of ethnic, cultural, linguistic and religious diversity. The region has witnessed violence due to various reasons ranging from secession to autonomy, movements against foreigners and immigrants, ethnic integration and looking back to their roots as a reaction to perceived imposition of Indianness.
- Punjab Terrorism: Punjab terrorism was the outcome of political ineptness and drew its strength and legitimacy not from any ideology or religious sanction but from the failures of political institutions, governance and administration. It, along with increased narcotic trade, still has the capacity to subvert the peace of the region.
- Left Wing Extremism: The uneven development pattern coupled with rising poverty and unemployment had prevailed in the interior regions of the country. This has created a very dangerous situation of Maoism/ Naxalism/Left Wing Extremism. In 2006, the then PM even regarded it as the biggest security threat to the nation.
Though the state has responded adequately to external threats, its responses to internal challenges have been largely inadequate. Our inner weaknesses and instability has – encouraged external threats and posed a serious challenge to National Security.
Ministry of Home Affairs (MoHA) and Internal Security:
There exist various organisations, laws and structures to deal with different aspects of security of India but the MoHA is the apex institution for internal security of the country. The MoHA has multifarious responsibilities. The most important among them being, internal security, border management, Centre-State relations, administration of Union Territories, management of Central Armed Police Forces, disaster management etc.
Mandate of MoHA:
Although, “public order” and “police” are State subjects under Schedule 7th of the Constitution, article 355 of the Constitution puts a responsibility on the Centre to prevent every state against external aggression and internal disturbance and to ensure that every Government of every State is carried on in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution. In pursuance of this mandate, MoHA performs the following tasks:
- Monitors the internal security situation
- Issues appropriate advisories
- Shares intelligence inputs
- Extends manpower and financial support
- Extends guidance and expertise to State Governments for maintenance of security, peace and harmony.
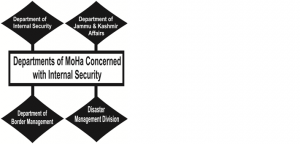
Departments of MoHA concerned with Internal Security
The various departments of MoHA concerning the security of the State are as follows:
- Department of Internal Security: The department deals with Indian Police Service, Central Armed Police Forces, Internal Security and Law and Order, insurgency, terrorism, Left Wing Extremism, activities of inimical foreign agencies, terrorist financing, rehabilitation, immigration issues and security clearances, maintenance of communal harmony, etc.
- Department of Jammu and Kashmir Affairs: It deals with all the Constitutional provisions relating to the State and welfare schemes implemented for the development to the State. It also ensures public order and security to be maintained in the State.
- Department of Border Management: It deals with management of international borders, including coastal borders, strengthening of border guarding and creation of related infrastructure, border areas development, etc.
- Disaster Management Division: The Division is responsible for legislation, policy, capacity building, prevention, mitigation, long term rehabilitation, response, relief and preparedness for natural calamities and manmade disasters (except drought and epidemics).