Current Affairs 09 October 2023
Today’s News
Tightrope walk: By not raising interest rates, RBI betrays its concerns about slowing growth
(Current Affairs 09 October 2023 | Relevant for GS Paper-3, Economic Growth)

- The decision of the RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) to leave interest rates unchanged even as the central bank warned of the major risk that ‘high inflation’ poses to macroeconomic stability is a clear sign that monetary authorities find themselves caught in a cleft stick.
- After a relatively benign first quarter, when headline retail inflation averaged 4.63% as against the RBI’s projection of 4.6%, price gains measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) accelerated sharply in the last quarter with July and August seeing readings of 7.44% and 6.83%, respectively.
- In a tacit acknowledgment of its misjudgment of inflationary trends, the MPC last week raised its projection for average second quarter inflation by 20 basis points, from the August forecast of 6.2% to 6.4%. And even this projection appears overly optimistic if one considers that the headline number will need to have slowed drastically to less than 5% in September for the RBI’s prognosis to be validated.
- The RBI’s unwillingness to walk the talk and raise interest rates further, even while reiterating the threat to overall economic stability from unmoored inflation expectations, reflects an unstated concern that the growth momentum still remains rather tenuous.
- The recent debate on the integrity of the NSO’s data on economic growth estimates, and concern that the methodology used to posit 7.8% real GDP growth in the first quarter may have given rise to an overestimation, have to be seen in tandem with economic forecasters’ increased caution over India’s GDP growth outlook for the current fiscal year.
- With the rupee already having weakened by about 0.7% since the last policy meeting in August, the RBI also runs the risk of importing inflation and adding to the external sector vulnerabilitie-s if it fails to raise interest rates.
How the Digital India Act will shape the future of the country’s cyber landscape
(Current Affairs 09 October 2023 | Relevant for GS paper-3, Cyber Security)
- Nations worldwide are grappling with the need to update their legal frameworks to adapt to the evolving digital landscape. India, with its ambitious ‘Digital India’ initiative, is no exception.
- The recent announcement of the Digital India Act 2023 (DIA) represents a significant step towards establishing a future ready legal framework for the country’s burgeoning digital ecosystem.
- The DIA, poised to replace the two decade old Information Technology Act of 2000 (IT Act), is designed to address the challenges and opportunities presented by the dramatic growth of the internet and emerging technologies.
- The primary motivation behind the DIA is to bring India’s regulatory landscape in sync with the digital revolution of the 21st century. The IT Act of 2000, crafted during a time when the internet was in its infancy, has struggled to keep pace with the rapid changes in technology and user behaviour.
- The nature of internet usage has also evolved, with the emergence of various intermediaries and the proliferation of new forms of user harm, such as cybers talking, trolling, and doxing.
- The DIA encompasses several pivotal clauses that mirror the dynamic evolution of the digital environment, addressing its multifaceted challenges and opportunities. These provisions underscore the legislation’s responsiveness to the ever changing digital landscape.
- The proposed DIA encompasses a spectrum of significant provisions aimed at addressing the ever evolving digital landscape. Firstly, it places a strong emphasis on online safety and trust, with a commitment to safeguarding citizen’s rights in the digital realm while remaining adaptable to shifting market dynamics and international legal principles.
- Secondly, recognising the growing importance of new age technologies such as artificial intelligence and block chain, the DIA provides guidelines for their responsible utilisation.
- This means that the DIA does not just leave it to the market to dictate the course of these technologies but actively engages in shaping their development and use within a regulatory framework. And by doing so, the DIA strikes a balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding against potential harms.
- This forward looking stance is not only beneficial for citizens and businesses but also positions India as a responsible player in the global technology landscape, ready to harness the full potential of new age technologies while mitigating associated risks.
- Thirdly, it upholds the concept of an open internet, striking a balance between accessibility and necessary regulations to maintain order and protect users.
- While the introduction of the DIA is a commendable step towards addressing the challenges of the digital age, there are certain aspects that warrant a critical evaluation.
- One key concern is the potential impact on innovation and the ease of doing business. Stricter regulations, particularly in emerging technologies, could inadvertently stifle entrepreneurial initiatives and deter foreign investments.
- Furthermore, the DIA’s success hinges on effective enforcement, which will require substantial resources, expertise, and infrastructure. Balancing the interests of various stakeholders, including tech giants, while ensuring the protection of citizen rights, poses a significant challenge.
- The DIA is a crucial step towards ensuring a secure, accountable, and innovative digital future for India. It represents a forward looking approach to regulation in an age of constant change and has the potential to shape the country’s digital landscape for generations to come.
Refresh Basics
Digital India Bill 2023
The primary objective of the Digital India Bill is to streamline and unify existing laws concerning the digital domain. It must be noted that this Bill will work in conjunction with other notable legislation and policies, such as the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, the National Data Governance Policy, the Indian Penal Code amendments for cybercrime, etc. Together, these laws and policies are set to establish a comprehensive framework aimed at governing different facets of the digital sphere in India.
The Digital India Bill encompasses the following key provisions:
- Classification of intermediaries: The Digital India Bill introduces a classification system for intermediaries, categorizing them into various groups based on their risk and size. These intermediaries include social media platforms, e-commerce platforms, AI platforms, and fact-checking platforms. By implementing this classification, the Bill allows for customized regulations that are specifically tailored to each category of intermediaries. This approach ensures that appropriate and relevant rules are applied to different types of intermediaries, taking into account their specific characteristics and potential impact on the digital ecosystem.
- Risk assessment for intermediaries: As per the Digital India Bill, intermediaries are mandated to perform risk assessments, which are then utilized to classify them based on their respective levels of risk. This classification system ensures that intermediaries are subject to appropriate regulations that match the level of risk they may pose in the digital space. By conducting these risk assessments, the Bill aims to implement targeted and effective measures for each category of intermediaries, promoting a balanced and secure digital environment.
- Establishing a dedicated internet regulatory authority: The Bill introduces the establishment of a dedicated internet regulator, akin to existing regulatory bodies, such as the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) or the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). This new regulator will be responsible for overseeing and managing internet-related matters, ensuring effective governance and compliance in the digital domain. Just like other regulatory bodies, the internet regulator’s primary focus will be to address and regulate various aspects of the online space, promoting fair practices, safeguarding user interests, and maintaining a well-regulated digital environment.
- Designating punishable offences: Under the Digital India Bill, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) is empowered to designate certain activities as punishable offences. These may include deliberate dissemination of misinformation, identity theft, cyber bullying targeting children, and other similar activities. By classifying these actions as offences, the Bill aims to address and combat the negative consequences of such misconduct in the digital space. This provision enables MeitY to take appropriate measures and establish legal frameworks to prevent and penalize individuals or entities involved in these harmful activities, promoting a safer and more responsible digital environment.
- Penalties for violations and user harms in emerging technologies: The Digital India Bill introduces penal provisions to tackle violations and user harm that may arise from emerging technologies, including generative AI platforms like Chat GPT. These provisions are designed to address any potential misuse, breaches of regulations, or negative consequences that may occur in the context of these technologies.
- Modifications to existing internet platform rules: As part of the provisions in the Digital India Bill, certain fundamental rules that currently apply to internet platforms, such as safe harbor norms, may undergo revisions or modifications. These changes aim to adapt the existing rules to the evolving digital landscape and address emerging challenges related to content moderation, liability, and user safety.
- Ensuring platform accountability: The Digital India Bill will legally empower the government to ensure that platforms are held accountable for hosting prohibited content. This includes content such as pornography, harmful material for children, copyright infringement, misleading information, impersonation, content that undermines India’s unity and integrity, computer malware, banned online games, and any other illegal material.
Using Gravity to Solve Power’s Problem
(Current Affairs 09 October 2023 |Relevant for Prelims, Science and Technology)

- Gravity-based energy storage is emerging as a solution to renewable energy intermittency and interruption, with the help of Energy Vault, which is in talks with Indian companies like NTPC, Tata Power, and ReNew Power.
- Energy Vault offers the EVx platform using gravity and mechanical elevators to store and release energy with 25-tonne blocks.
- It also focuses on short-term storage, eco-friendly materials, and green hydrogen energy storage.
- India’s push for renewable power makes energy storage crucial as its renewable energy growth presents challenges for grid managers.
- Most energy storage worldwide comes from pumped hydro, but alternative solutions are being explored.
- The Indian government is considering hydrogen and hybrid generation models for energy storage.
- Efforts are being made to identify pumped hydro sites, including potential use of opencast mines.
Enzyme Mimetic to Degrade Pollutants in Waste-Water
(Current Affairs 09 October 2023 | Relevant for Prelims, Science and technology, GS paper-3, Nano technology and applications)
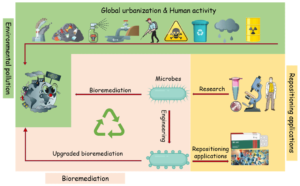
- Recently, Scientists at Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Materials Research Centre developed a sunlight-driven enzyme mimetic for wastewater treatment.
- The study introduced a platinum-containing nano zyme called Nano PtA.
- Nano Pt A forms tape-like structures when in contact with wastewater and emits light to degrade pollutants.
- It can degrade common effluents in ten minutes under sunlight and remains stable for up to 75 days.
- Nanozyme may find applications in healthcare, particularly for neurological diseases.
- Natural enzymes face limitations like sensitivity, complex production, and storage issues.
- Nanozymes can overcome these challenges and mimic natural enzymes.
Platypuses
(Current Affairs 09 October 2023 | Relevant for Prelims, Biodiversity, conservation efforts)

- Recent research sheds light on a troubling situation related to water-dwelling animal, Platypuses (Ornithorhynchus anatinus), following the 2019–20 Black Summer bushfires in eastern Australia.
- Platypuses are unique to Australia. Its streamline body and a broad, flat tail are covered with dense waterproof fur, which provides excellent thermal insulation.
- They possess webbed feet for swimming and electroreceptors in their bills to find food in rivers and streams.
- Along with echidnas, Platypuses are grouped in a separate order of mammals known as monotremes, which are distinguished from all other mammals because they lay eggs.
- Also, males have a venomous spur on their ankles, a unique feature among mammals, that they primarily used during the breeding season.
While not lethal, the venom can cause severe pain and swelling in humans.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Platypuses inhabit freshwater systems across a wide range of Australian landscapes.
- They can be found in tropical rainforest lowlands, plateaus of northern Queensland, and even cold, high-altitude regions like Tasmania and the Australian Alps.
Seasonality and Behavior:
- Platypuses are active year-round, with a preference for twilight and nighttime activity.
- Platypuses spend much of their time in burrows along riverbanks or in rocky crevices and stream debris.
Feeding Habits:
- Platypuses primarily feed at night on a wide variety of aquatic invertebrates.
- They feed on insect larvae, shrimps, swimming beetles, water bugs, tadpoles, worms, and more.
- Larger prey is taken individually and consumed after floating on the water surface.
Predators and Threats:
- Predators include crocodiles, goannas, carpet pythons, eagles, and large native fish.
- Land-based predators like foxes, dogs, and dingoes may pose a threat. Ectoparasites, tick species, and fungal infections can also affect platypuses.
Conservation Status:
IUCN Red List: Near Threatened.
Related Blogs…
 |
 |
GS Related Practices Question…
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques.
META TAGS:
Current affairs 09 October 2023, Current affairs 07 October 2023, Today news, Today news GS, Today news upsc, Today news and views, Today news 2023, Today news Current affairs September 2023, Current affairs news, Current affairs book pdf, Current affairs best blog, Current affairs for UPSC, Current affairs 2023, Current affairs contact, Current affairs book, Current affairs program meaning

Choose The Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “which optional subject is the best?” and “which optional subject is the most scoring?” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher, is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains, which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular
Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers.”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional, you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey, potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher. Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques. Sociology, Social theory, Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Sociology Optional Syllabus.
Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Sociology Syllabus, Sociology Optional, Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Course, Sociology Teacher, Sociology Foundation, Sociology Foundation Course, Sociology Optional UPSC, Sociology for IAS,
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
🔎https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology
Find More Blogs…
| Compare and contrast Karl Marx’s and Max weber’s | Karl Marx- Historical Materialism |
| Talcott Parsons : Social system | Scope of the subject and comparison with other social sciences |








2 comments