Relevance: Prelims/Mains: G.S paper III: Environment and Ecology
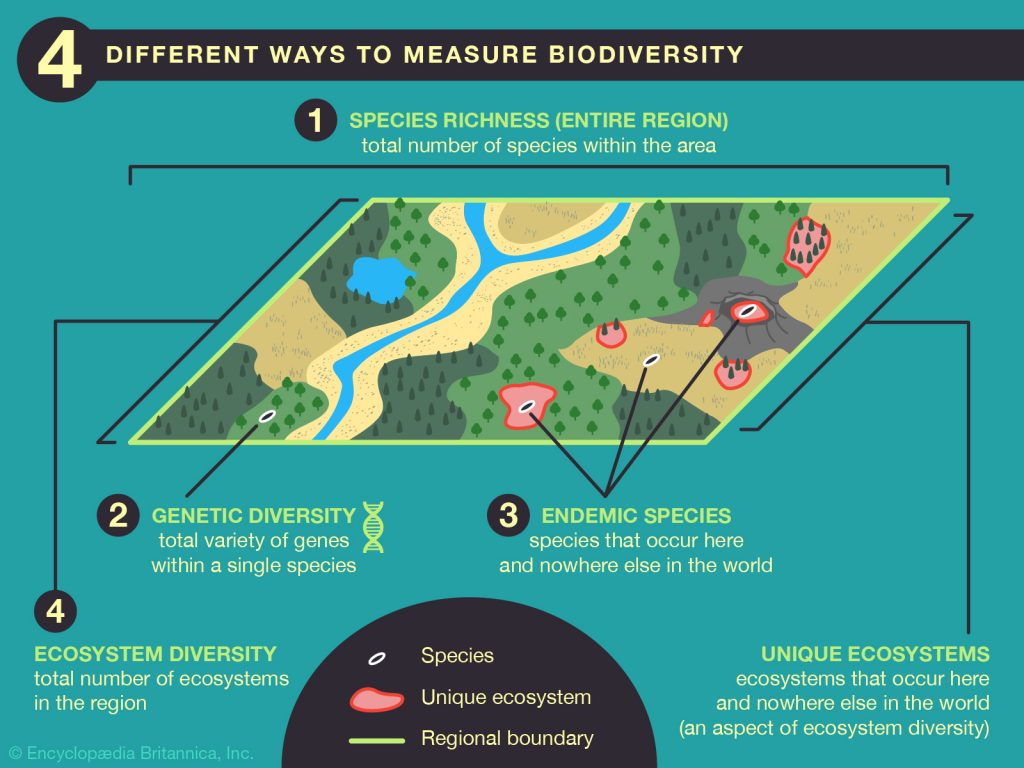
►BIODIVERSITY
Also known as Biological diversity is a term that describes the variety of living beings on Earth. In short, it is described as degree of variation of life. Biological diversity encompasses microorganism, plants, animals and ecosystems such as coral reefs, forests, rainforests, deserts etc.
►ECOLOGY
- It is the scientific study of the distributions, abundance and relations of organisms and their interactions with the environment.
- Ecology includes the study of plant and animal populations, plant and animal communities and ecosystems.
- Ecosystems describe the web or network of relations among organisms at different scales of organization.
- Since ecology refers to any form of biodiversity, ecologists research everything from tiny bacteria’s role in nutrient recycling to the effects of tropical rain forest on the Earth’s atmosphere.
►ENVIRONMENT
The environment comprises of:
- Biotic – Living organisms comprising of plants, animals, microbes etc.
- Abiotic – Inorganic and non -living parts of an ecosystem (Energy, Rainfall, Temperature etc.)
- Biotic Community comprises of: Autotrophs (Primary Producers) and Heterotrophs (Primary Consumers)
- Heterotrophs (Consumers) are of two types: Macro Consumers (feed on plants or animals or both) and Micro Consumers (Saprotrophs – Decomposers)
►ECOSYSTEM
- An ecosystem consists of a community of organisms together with their physical environment.
- It is the interaction of living and nonliving things in an environment.
- Diverse: Ecosystems can be of different sizes and can be marine, aquatic, or terrestrial. Broad categories of terrestrial ecosystems are called biomes.
- In ecosystems, both matter and energy are conserved. Energy flows through the system—usually from light to heat—while matter is recycled.
- Matter is recycled;
- Energy flows through the ecosystem, usually entering as light and exiting as heat.
- Ecosystems with higher biodiversity tend to be more stable with greater resistance and resilience in the face of disturbances, disruptive events.
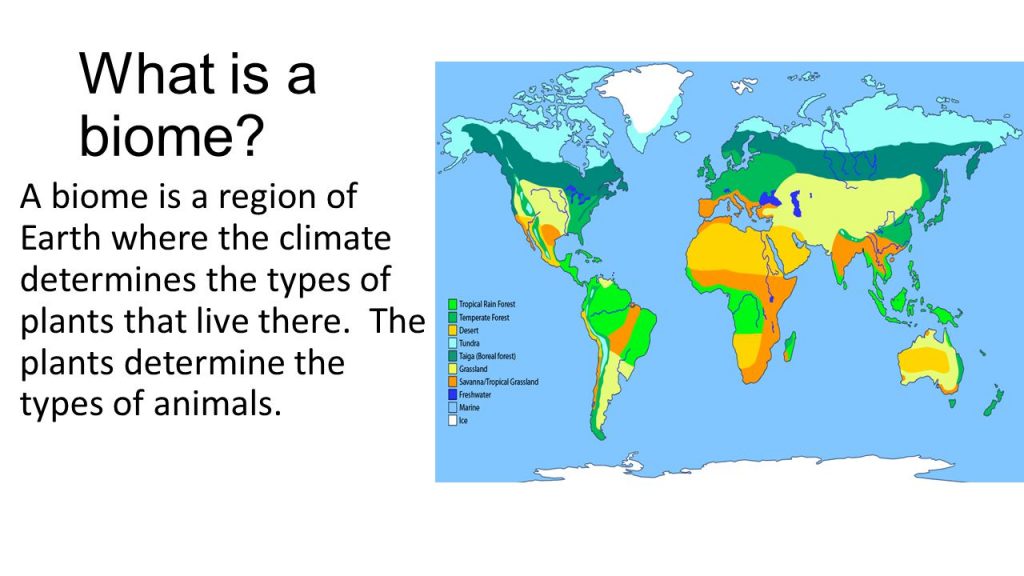
►BIOME
- A biome is a community of plants and animals that have shared physical climate.
- A biome is different from an ecosystem.
- Temperature, soil, and the amount of light and water help determine what life exists in a biome.
- A number of Biomes exist such as – Tropical Deserts, Savannas, Tropical Rainforests, Temperate Grasslands, Arctic Tundra, Freshwater Biomes, Marine Biomes, etc.
For more such notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel.
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC –Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php