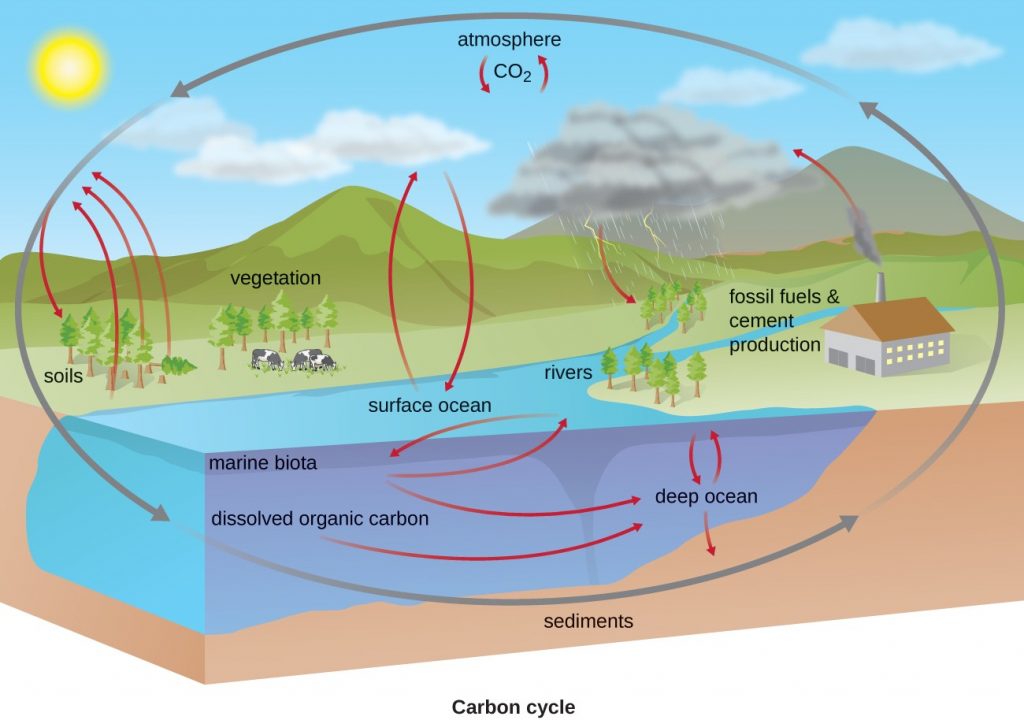
►BIO-GEO CHEMICAL CYCLE
- A pathway by which a chemical substance moves through biotic (biosphere) and abiotic (lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) compartments of Earth.
- There are biogeochemical cycles for carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and water; and there are human-induced cycles such as those for mercury and atrazine.
- In this cycle energy is finally lost as heat while nutrient keep on recycling.
►ECOLOGICAL NICHE
- In ecology, a niche is a term describing the relational position of a species or population in an ecosystem.
- More formally, the niche includes how a population responds to the abundance of its resources and enemies (e. g., by growing when resources are abundant, and predators, parasites and pathogens are scarce) and how it affects those same factors (e. g., by reducing the abundance of resources through consumption and contributing to the population growth of enemies by falling prey to them).
- The abiotic or physical environment is also part of the niche because it influences how populations affect, and are affected by, resources and enemies.
- The description of a niche may include descriptions of the organism’s life history, habitat, and place in the food chain.
- According to the competitive exclusion principle, no two species can occupy the same niche in the same environment for a long time.
►ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION
- A process of directional change in vegetation on an ecological time scale.
- In this process, a series of communities replace one another due to large scale natural or anthropogenic destructions.
TYPES OF ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION
- Primary Succession: When a terrestrial site is first colonised by the pioneer species.
- Secondary Succession: After Climax (destruction of an existing site), the sequential development of biotic communities.
- Examples of succession:
For terrestrial land: Bare rocks – Lichens — Annual Plants — Perennial Plants and Grasses – Shrubs – Softwood Tress, Pines – Hardwood trees
- For Hydrosere: Phytoplankton – submerged plant stage – Submerged free floating plant stage – Reed swamp stage(Sedge) – Marsh meadow stage – Scrub stage – Forest
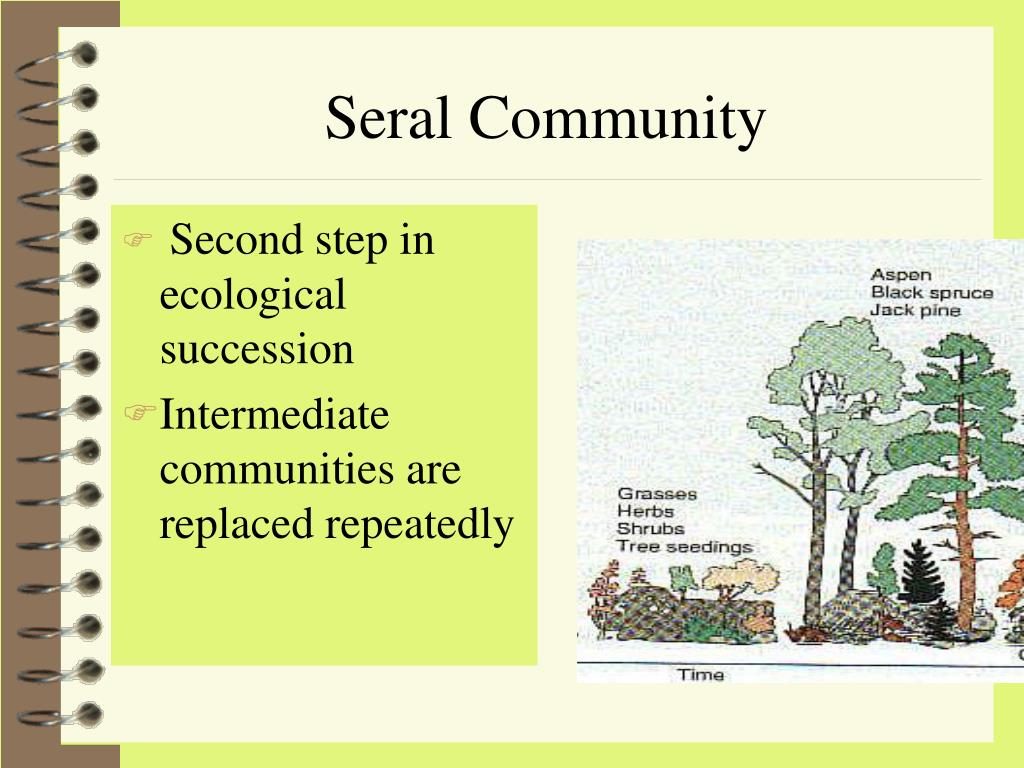
SERAL COMMUNITY (SERE)
An intermediate stage found in ecological succession in an ecosystem advancing towards its climax community.
For more such notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel.
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC –Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php