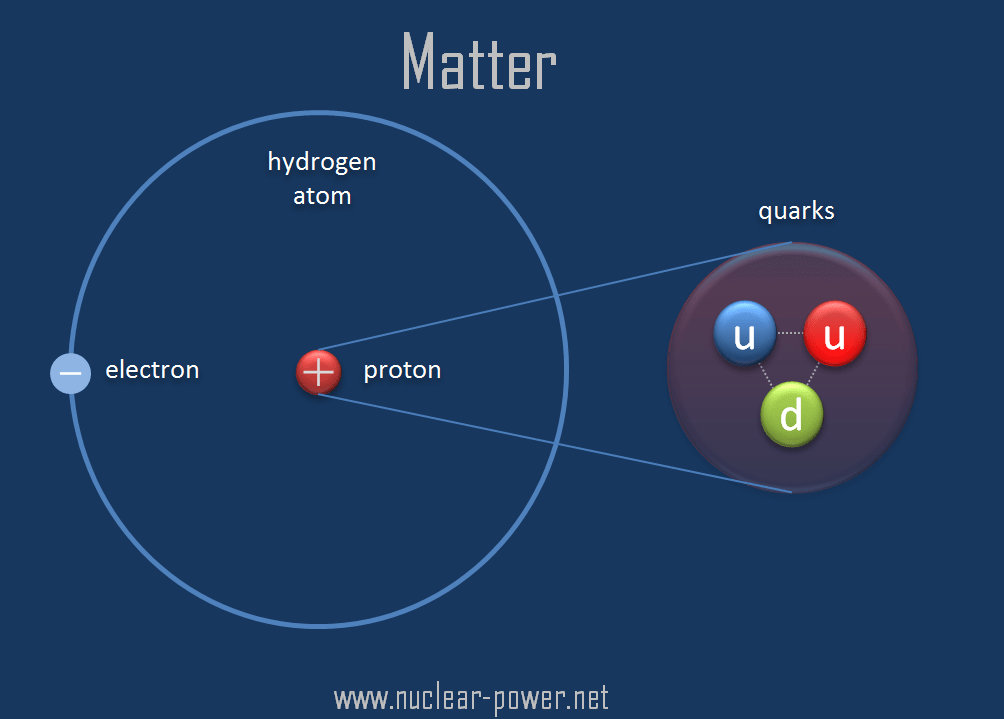
►STANDARD MODEL OF PHYSICS
The standard model identifies elementary particles into Quarks, Leptons and Bosons.
►ANTIMATTER
Every known matter has an antimatter which has the same mass and volume; only difference being the inherent charge. Antimatter has an opposite charge when compared to its matter. While the Anti-matter of a proton is called Anti-
Proton, the Antimatter of an electron is called Positron.
►QUARKS
- Quarks are elementary particles propounded in the standard model.
- They join to form hadrons, such as protons and neutrons, which are components of the nuclei of atoms.
- The antiparticle of a quark is the antiquark.
- There are 6 principal quarks and, hence, 6 anti quarks.
- Quarks and antiquarks are the only two fundamental particles that interact through all four fundamental forces of physics: gravitation, electromagnetism, and the strong interaction and weak interactions.
- A quark exhibits confinement, which means that the quarks are not observed independently but always in combination with other quarks.
- This makes determining the properties (mass, spin, and parity) impossible to measure directly.
►LEPTONS
- Like quarks, leptons too are of 6 types. However, they do not have any fractional charge. The leptons are:
ELECTRON, MUON, TAU and 3 Types OF NEUTRINOS
- Electron being a Lepton is a fundamental elementary particle.
►FERMION
- Fermions are particles which have half-integer spin and therefore are constrained by the Pauli exclusion principle. Particles with integer spin are called bosons. Fermions include electrons, protons, neutrons.
- Fermions include all quarks and leptons.
- The fact that electrons are fermions is foundational to the building of the periodic table of the elements since there can be only one electron for each state in an atom (only one electron for each possible set of quantum numbers).
- The fermion nature of electrons also governs the behaviour of electrons in a metal where at low temperatures all the low energy states are filled up to a level called the Fermi energy.
►BOSON
Boson is a collective name given to particles that carry forces. It has been named after Indian scientist Satyendra Nath Bose. Gravity as a force of nature is yet not accepted by the Standard Model due to the failure to discover its Boson. Strong Nuclear Force is the strongest known force while gravity is the weakest.
►GOD PARTICLE
- Peter Higgs suggested that particles did not have mass just after Big Bang. As the universe cooled and temperature fell below the critical point, an invisible force field got formed which has been termed the Higgs Field.
- The associated particles with the Higgs field have been termed the Higgs Boson. It has been theorized that any particle that interacted with these Higgs Boson got mass and those particles that were left out of the Higgs field remained massless.
- As these Higgs Bosons have the capability to grant mass, the primary condition for the existence of matter, they were termed as the God particle.
- The Big Bang Theory is the leading explanation about how the universe began. It talks about the universe as we know it starting with a small singularity, then inflating over the next 13.8 billion years to the cosmos that we know today.
- Recently, Scientist at CERN observed the Higgs boson decaying to fundamental particles known as bottom quarks.

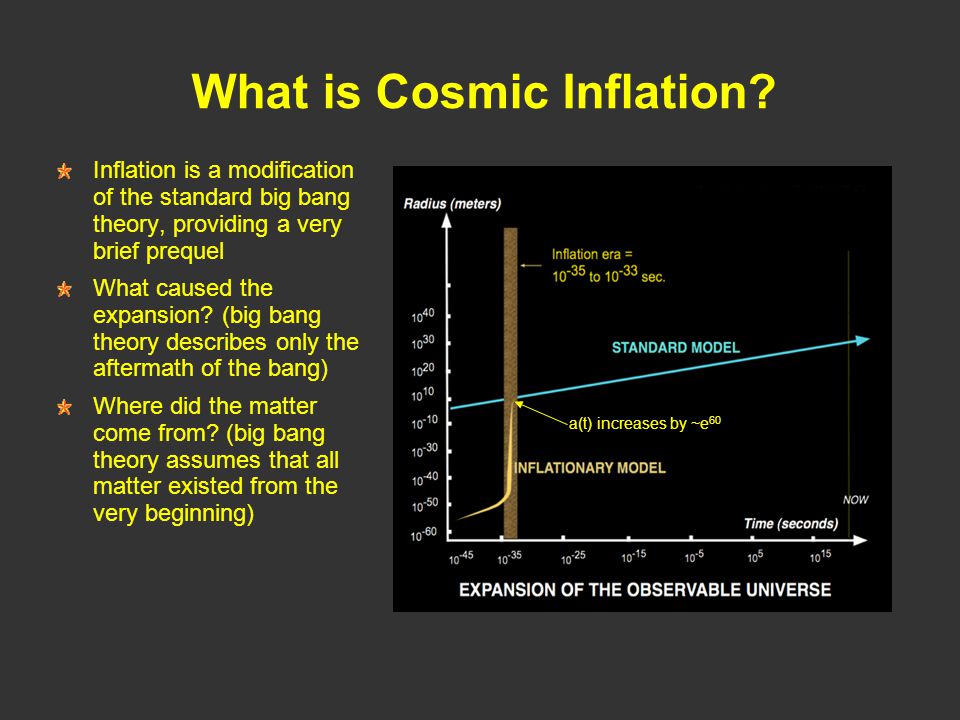
►COSMIC INFLATION
Alan Guth in 1981 gave his theory of Cosmic Inflation. According to this theory, just after the Big Bang, there was a phase of very rapid expansion of universe at a speed greater than light which sent ripples (primordial gravitational waves) that are responsible for the polarization of the universe causing stretching and squeezing of the cosmic space.
For more such notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel.
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC –Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php