Paper 2: Government policies & interventions for development in various sectors & issues arising out of their design & implementation
5.5 lakh beneficiaries under PM Rojgar Protsahan Yojana
- The government is adding about 5.5 lakh beneficiaries a month under the Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY), a scheme started to incentivize employers for generation of new employment wherein the Government of India pays the employer’s contribution of Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS) for the new employment. The annual average addition of workers under the scheme is expected to be over 66 lakhs.
About the scheme
- PMRPY scheme was started to incentivize employers for generation of new employment wherein the Government of India pays the employer’s contribution of Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS) for the new employment
- Under the scheme, the government was paying the employers’ contribution of 8.33 percent of wages to the Employees’ Pension Scheme (EPS) for new employees having a new Universal Account Number (UAN) and who joined on or after April 1, 2016 with salary up to Rs 15,000 per month — for first three years
- The PMRPY scheme was started in August 2016
- The scheme is aimed at incentivizing increasing the employment base of workers in the establishments and facilitate access to social security benefits of the organized sector
Paper 2: Important International institutions, agencies & fora, their structure, mandate
UN Council Seats Elections
Why in News
- Germany and Belgium are certain to win seats on the U.N. Security Council after Israel dropped out of the race last month
- The Maldives, a small island nation that has never been on the U.N.’s most powerful body, was vying for a seat against Indonesia, the world’s largest Muslim country, which has served on the council three times
Why winning a Seat is important ?
- Winning a seat on the Security Council is a pinnacle of achievement for many countries because it gives them a strong voice in matters dealing with international peace and security ranging from conflicts in Syria, Yemen and South Sudan to the nuclear threat posed by North Korea and attacks by extremist groups such as the Islamic State and al-Qaeda.
UN Security Council
- The Security Council has five permanent members the United States, Russia, China, Britain and France
- 10 members are elected by the 193-member General Assembly for two-year terms
- Five countries are elected every year by secret ballot
Uncontested slates
- Candidates for non-permanent seats are chosen by regional groups
- The only contested race this year is for the Asia-Pacific group’s seat
- The other regions have uncontested slates, and their candidates are virtually assured of victory for two-year terms
- These are:
- Belgium and Germany for the Western European and Others group of nations
- South Africa for the Africa group
- The Dominican Republic for the Latin America and Caribbean group
US Sanctions and Iran’s Nuclear Plans
What is the issue?
- Iran has notified IAEA of it nuclear enrichment plans.
- Iran should cooperate with Europe and China to work around U.S. sanctions.
What is Iran’s stance?
- Iran said that it was in “preparatory works” to restart nuclear activities.
- This is in the event of the failure of the 2015 accord.
- In such a scenario, Iran could restart its activities without any limits.
- The preparatory works mentioned refer to steps to boost uranium enrichment capacity by producing new centrifuges.
- In addition, it had notified of a plan to restart activity at its uranium conversion facility to produce the UF6 feedstock for centrifuges
What are the other developments in this regard?
- France, Britain, Germany and the EU have sent a joint official request to the U.S.
- It asks for their companies to be exempt from punitive measures resulting from fresh U.S. sanctions on Iran.
- It calls for exempting European businesses doing legitimate trade in Iran from all extraterritorial American sanctions.
What are the implications?
- Iran’s notification illustrates the risks associated with the recent U.S. withdrawal from the nuclear deal.
- According to the deal, Iran can enrich uranium, but under tight restrictions.
- It would not be technically violating the agreement as long as it does not produce centrifuges.
- But the move to open a production facility could be seen as a provocative step by the remaining parties to the agreement.
- The other signatories to the deal said they remain committed to the agreement.
- But they are yet to come up with a framework to continue the deal.
- The latest Iranian announcement could pressurize the European powers.
- They are forced to come up with guarantees that the deal’s benefits will be in place even with U.S. sanctions.
Alteration in India’s Foreign Policy
What is the issue?
- In recent times India is trying to re calibrate its relation with global economic powers.
- But India approach with US relations is not quite balancing out.
What foreign policy priorities of India concerns US?
- India maintains good relation with the U.S., Russia and China in equal measure.
- Where USA vowed to counter China’s moves in the Indo-Pacific, and U.S. National Defence Strategy puts both China and Russia in its crosshairs as the world’s two “revisionist powers”.
- A year ago, India seemed clear in its intention to counter China’s growing clout in its neighborhood, especially post-Doklam, challenge the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and back a Quadrilateral grouping of India, the U.S., Japan and Australia to maintain an open Indo-Pacific.
- But India’s stand has changed in recent times as the Doklam issue has been buried, the BRI isn’t as much a concern as before.
- The government’s non-confrontational attitude to the Maldives and Nepal also indicates a softened policy on China in the neighborhood.
- Recently India also rejected an Australian request to join maritime exercises along with the U.S. and Japan.
- Contrast to this is India’s acceptance of military exercises with countries of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), the Russia-China led grouping.
What will be implications of India’s policy?
- US had come to accept India’s diffidence on signing outstanding India-U.S. foundational agreements.
- US has now confused as India publicly enters the international arena in the corner with Russia and China, while proclaiming its intention to continue energy deals with Iran and Venezuela in defiance of American sanctions.
- Trade protectionism is clearly the other big point of divergence between India and the U.S., which have in recent months taken each other to the World Trade Organisation on several issues.
- There has been a surge in disputes between the two countries on the new American steel and aluminium tariffs.
- USA’s actions on CAATSA and Iran nuclear deal have also had a direct impact on India, given its high dependence on defence hardware from Russia and its considerable energy interests in Iran.
Paper 3: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment
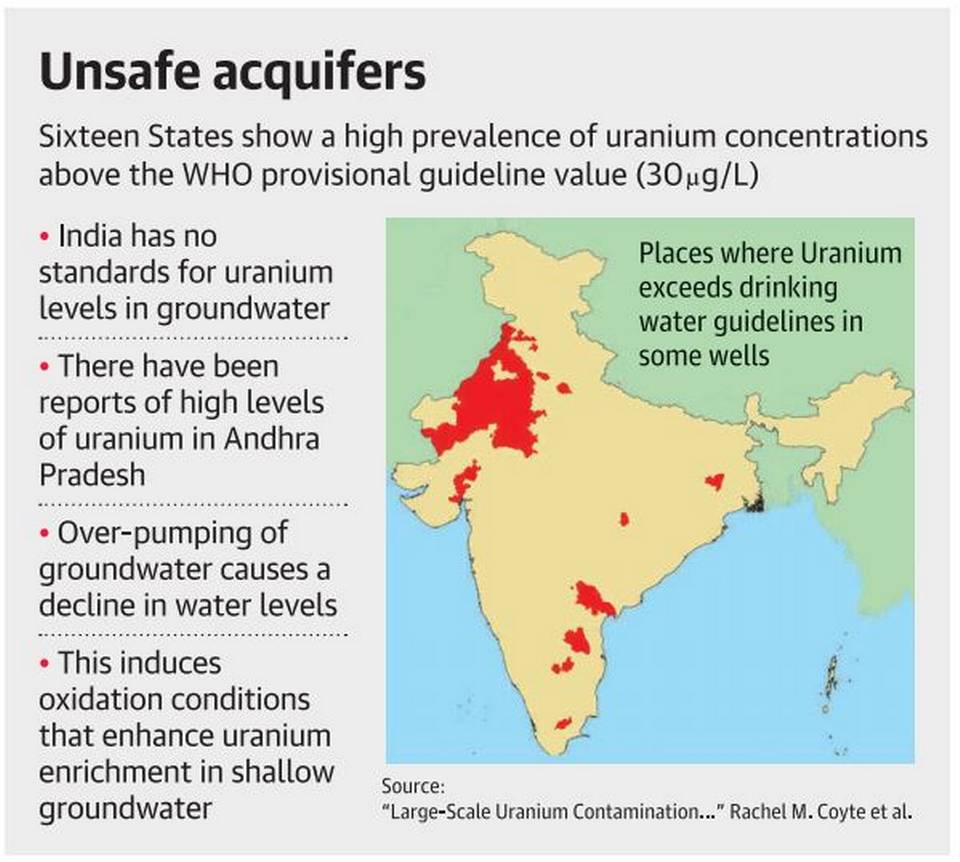
High uranium in Indian aquifers
Why in News?
- Study has found widespread uranium contamination in groundwater from aquifers in 16 Indian states. The main source is natural, but human factors such as groundwater-table decline and nitrate pollution may be exacerbating the problem
Risk factor
- Several studies have linked exposure to uranium in drinking water to kidney diseases. The World Health Organisation has set a provisional safety standard of 30 microgrammes of uranium per litre. Uranium is not, however, included in the list of contaminants monitored under the Bureau of Indian Standards’ Drinking Water Specifications, the study stated.
Where it was high in number
Likely Cause
- Factors contributing to the contamination include the amount of uranium in an aquifer’s rocks and various chemical interactions between rock and water. In many parts of India, these factors co-occur and result in high uranium concentrations in groundwater
- Human activities, especially over-exploitation of groundwater for irrigation, may have exacerbated the problem. Many of India’s aquifers are composed of clay, silt and gravel carried down from the Himalayas by streams or uranium-rich granitic rocks.
- When overpumping of these aquifers’ groundwater occurs and their water levels decline, it induces conditions that enhance uranium enrichment in the shallow groundwater that remains.
What can be done
- There is a need to revise current water-quality monitoring programmes in India and re-evaluate human health risks in areas of high uranium prevalence.
- Including a uranium standard in the Bureau of Indian Standards’ Drinking Water Specification based on uranium’s kidney-harming effects, establishing monitoring systems to identify at-risk areas, and exploring new ways to prevent or treat uranium contamination will help ensure access to safe drinking water for tens of millions in India
Paper 3: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
ISRO’s EPIC Planet
Context:
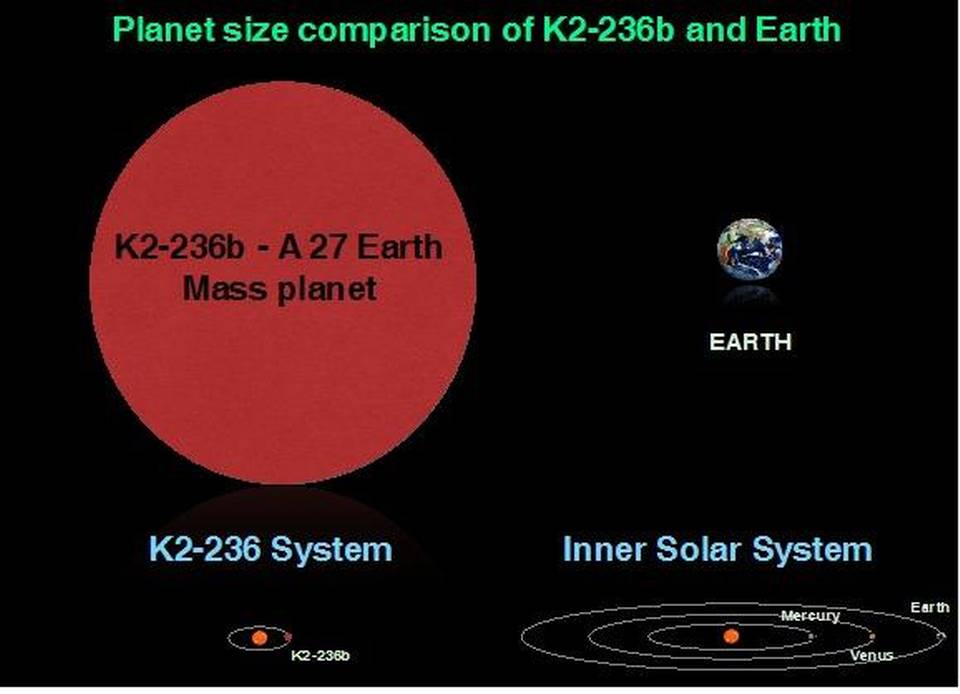
- In an epic Indian discovery, a team from the Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad, has spotted for the first time a distant planet six times bigger than Earth and revolving around a Sun-like star about 600 light years away. Both the planet and the star have been named EPIC.
About EPIC
- EPIC was found circling very close to the Sun-like star, going around it once in about 19.5 days and unlikely to be inhabitable because of its high surface temperature of around 600°C.
- The team found the planet to be smaller in size than Saturn and bigger than Neptune.
- Its mass is about 27 times Earth’s and six times that of Earth at radius.
- The scientists estimate that over 60% of its mass could be made up of heavy elements like ice, silicates and iron.
Why this Discovery is Important
- With this discovery India has joined a handful of countries which have discovered planets around stars,
- Significantly, the discovery was made using a PRL-designed spectrograph, PARAS, to measure and confirm the mass of the new planet.
- EPIC 211945201b (or K2-236b) is the name given to the planet.
Spectrograph studies
- The spectrograph is the first of its kind in the country which can measure the mass of a planet going around a star. Very few such spectrographs exist around the world (mostly in the USA and in the Europe) that can do such precise measurements.
- The scientists observed the target over a time 420 days or about 1.5 years. They measured the mass of the planet using the indigenously designed PRL Advance Radial-velocity Abu-sky Search or PARAS spectrograph integrated with the 1.2-metre telescope located at PRL’s Gurushikhar Observatory in Mount Abu, Rajasthan.
- PRL, described as the cradle of space sciences in India, conducts fundamental research in a host of physical sciences including astronomy and space.
- “Such a discovery is of importance for understanding the formation mechanism of such super-Neptune or sub-Saturn kind of planets that are too close to the host star.” The detection also adds to a sparse catalogue of 22 other confirmed exoplanet systems that have a mass and radius in this range.