Why in news?
• The principal reason that led to the recent 20,000-tonne oil leak at Norilsk at an Arctic region power plant in Russia is the sinking of ground surface due to permafrost thaw. The plant is built entirely on permafrost, whose weakening over the years due to climate change caused the pillars supporting a fuel tank at the plant to sink.
Permafrost:
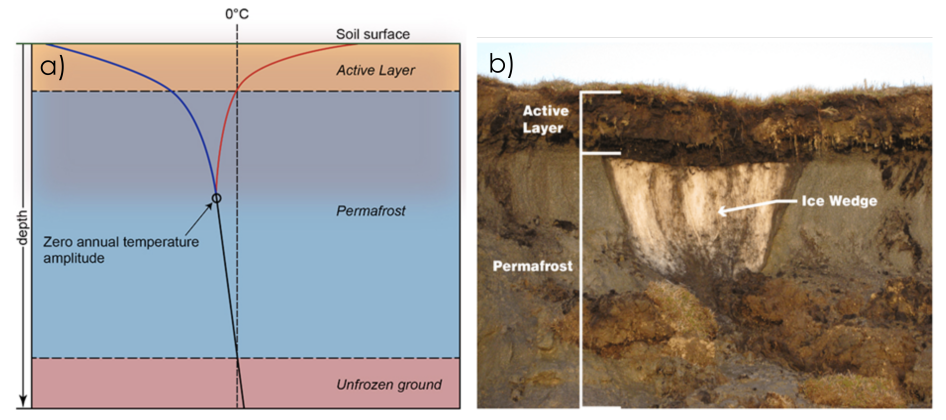
• Permafrost is any ground that remains completely frozen—32°F (0°C) or colder—for at least two years straight. It is defined solely based on temperature and duration.
• These permanently frozen grounds are most common in regions with high mountains and in Earth’s higher latitudes—near the North and South Poles.
• Permafrost covers large regions of the Earth. Almost a quarter of the land area in the Northern Hemisphere has permafrost underneath.
Composition:
• Permafrost is made of a combination of soil, rocks and sand that are held together by ice. The soil and ice in permafrost stay frozen all year long.
• Near the surface, permafrost soils also contain large quantities of organic carbon—a material leftover from dead plants that couldn’t decompose, or rot away, due to the cold. Lower permafrost layers contain soils made mostly of minerals.
• A layer of soil on top of permafrost does not stay frozen all year. This layer, called the active layer, thaws during the warm summer months and freezes again in the fall.

Impact of Climate Change on Permafrost:
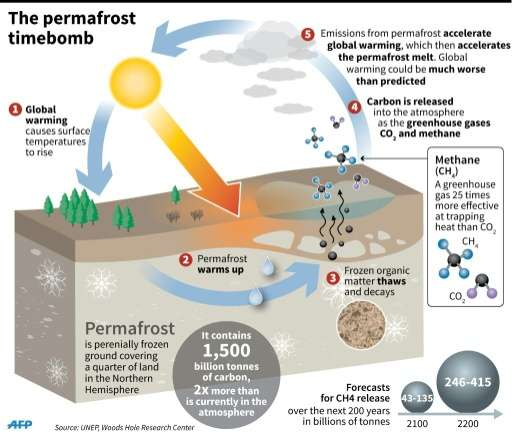
• As Earth’s climate warms, the permafrost is thawing. That means the ice inside the permafrost melts, leaving behind water and soil. Thawing permafrost can have dramatic impacts on our planet.
• Many northern villages are built on permafrost. Thawing permafrost can destroy houses, roads and other infrastructure.
• When permafrost is frozen, plant material in the soil—called organic carbon—can’t decompose, or rot away. As permafrost thaws, microbes begin decomposing this material which releases greenhouse gases the atmosphere.
• When permafrost thaws, so do ancient bacteria and viruses in the ice and soil. These newly-unfrozen microbes could make humans and animals very sick.

For more such notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel.
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC –Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php

