►ECOTONE
- A transition area between two biomes.
- It is where two communities meet and integrate. For ex -Mangroves, Estuary.
►BIOSPHERE
The layer of the planet Earth where life exists.
►BIOMASS
It is the amount of living or organic matter present in an organism.
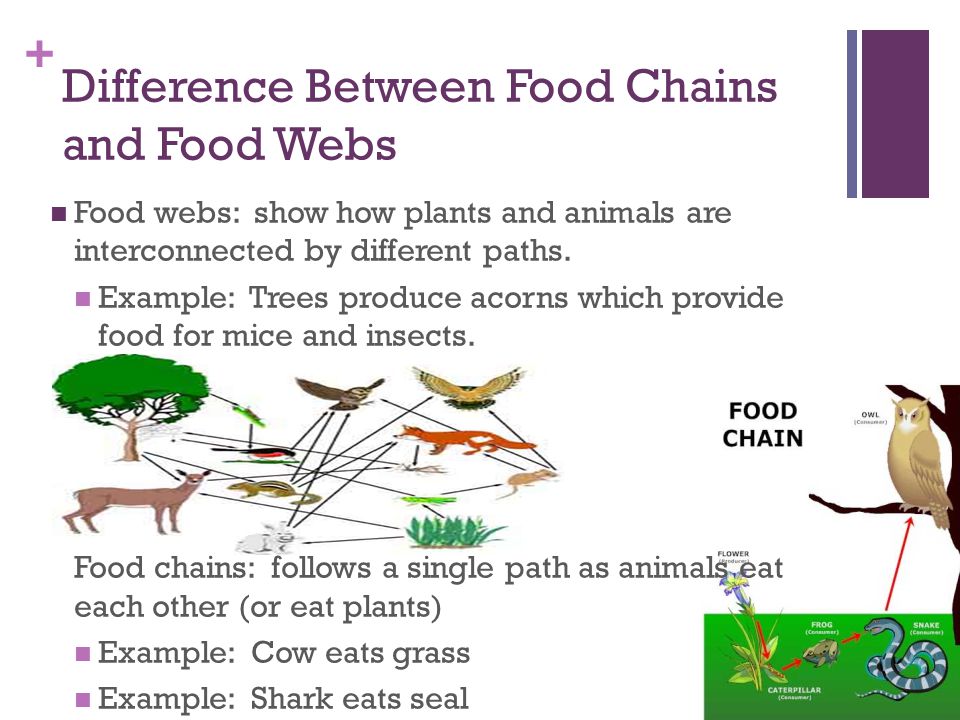
►FOOD CHAIN & FOOD WEB
- A FOOD CHAIN is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another.
- In a food chain, each organism occupies a different trophic level, defined by how many energy transfers separate it from the basic input of the chain.
- FOOD WEBS consist of many interconnected food chains and are more realistic representation of consumption relationships in ecosystems.
- Producers, or autotrophs, make their own organic molecules.
—Photoautotrophs, such as plants, use energy from sunlight to make organic compounds —sugars—out of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis.
—Chemoautotrophs use energy from chemicals to build organic compounds out of carbon dioxide or similar molecules. This is called chemosynthesis.
- Consumers, or heterotrophs, get organic molecules by eating other organisms.
- Types of food chain
–Grazing food chain
–Detritus food chain
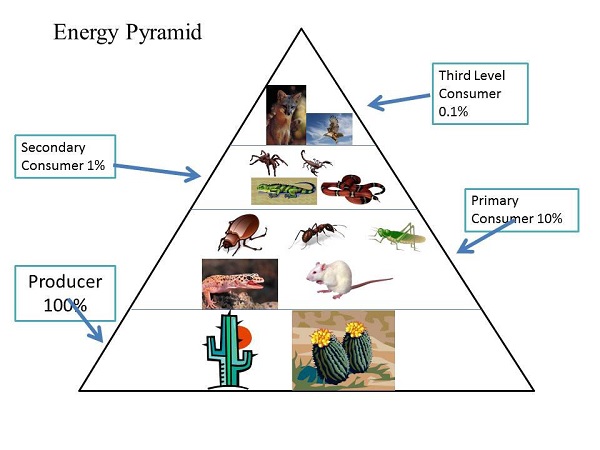
►ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS
- An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of the relationship between different organisms in an ecosystem.
- Energy moves up the pyramid, starting with the primary producers, or autotrophs, such as plants and algae at the very bottom, followed by the primary consumers, which feed on these plants, then secondary consumers, which feed on the primary consumers, and so on.
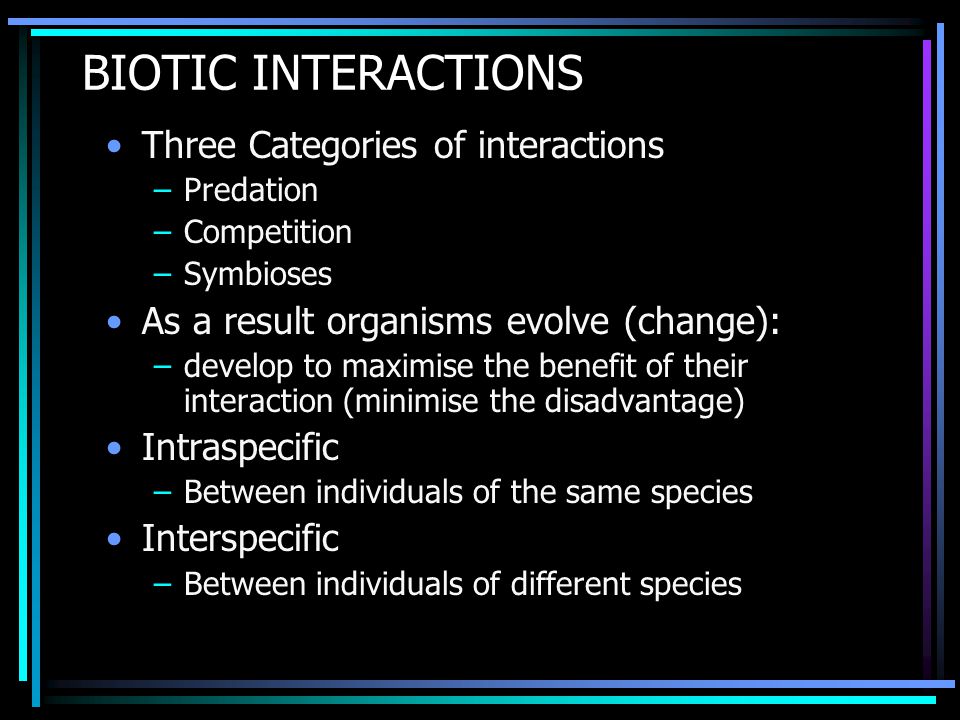
►BIOTIC INTERACTION
- Biotic interactions are the various mechanisms in which organisms interact with each other.
- Types of Biotic interactions
—Mutualism – Both species benefit.
—Commensalism – One species benefits, other is unaffected.
—Competition – Both species are harmed by the interaction.
—Predation and Parasitism – One species benefits and other is harmed.
—Amensalism – One species is harmed and other is unaffected.
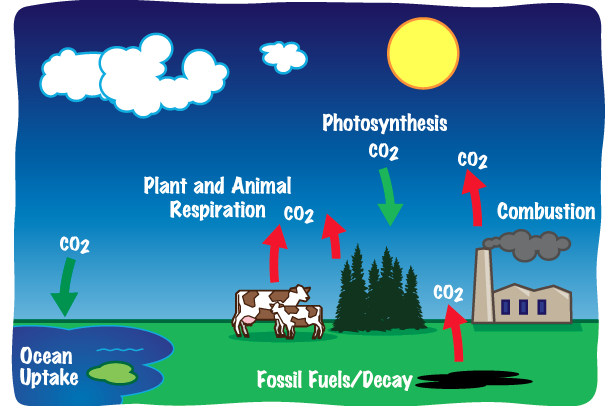
►BIO-GEO CHEMICAL CYCLE
- A pathway by which a chemical substance moves through biotic (biosphere) and abiotic (lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) compartments of Earth.
- There are biogeochemical cycles for carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and water; and there are human-induced cycles such as those for mercury and atrazine.
- In this cycle energy is finally lost as heat while nutrient keep on recycling.
For more such notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel.
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC –Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php