Relevance: Prelims: Economy
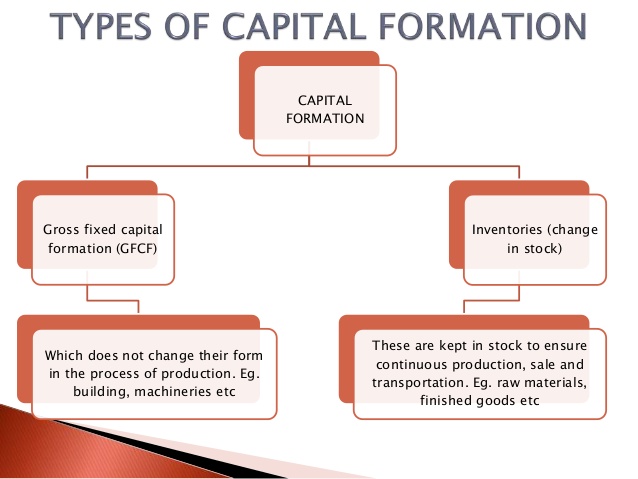
What is Gross Fixed Capital formation?
- It is essentially net investment.
- It is a component of the Expenditure method of calculating GDP.
WHAT IT INCLUDES?
- Land improvements (fences, ditches, drains, and so on); plant, machinery, and equipment purchases; the construction of roads, railways, private residential dwellings, and commercial and industrial buildings.
- Disposal of fixed assets is taken away from the total.
WHAT IT EXCLUDES?
- Land Purchases
- Effects of depreciation (referred to as consumption of capital)
MACROECONOMIC IMPACT
- In macro theory, a rise in investment should contribute towards higher aggregate demand and also increase productive capacity.
- Increasing investment should lead to higher economic growth in the long-term though it depends on how effective the investment is.
- Opportunity cost of investment: The opportunity cost of gross fixed capital investment is lower consumption – at least in the short-term. If more resources are spent on capital goods, it leads to decline in consumption of consumer goods.
For more such notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel.
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC –Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php